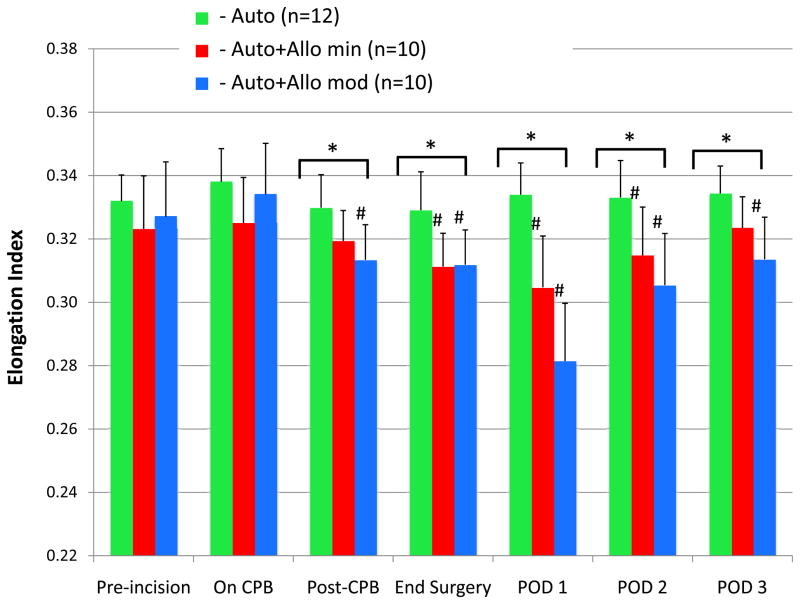
Figure 1.
Red blood cell (RBC) deformability, represented as the elongation index measured by ektacytometry, is compared among the 3 groups. In patients who received autologous salvaged RBCs only, elongation index did not change from baseline over the 3-day study period. For patients who received autologous salvaged RBCs and <5 units stored allogeneic RBCs, the mean elongation index decreased by 6%, reached a nadir on postoperative day (POD) 1, and remained significantly lower than baseline until POD 2. For those who received autologous salvaged RBCs and ≥5 units stored allogeneic RBCs, the mean elongation index decreased by 14%, reached a nadir on POD 1, and remained significantly lower than baseline for all 3 postoperative days. The findings illustrate a “dose-response” for decreasing RBC deformability with increased number of stored allogeneic RBC transfusions.
Auto = autologous salvaged RBCs only.
Auto+Allo min = autologous salvaged RBCs + minimal (<5 units) stored allogeneic RBCs.
Auto+Allo mod = autologous salvaged RBCs + moderate (≥5 units) stored allogeneic RBCs.
CPB = cardiopulmonary bypass.
*P < 0.05 for between-group differences; #P < 0.05 for within-group difference from pre-incision baseline.