Fig. 1.
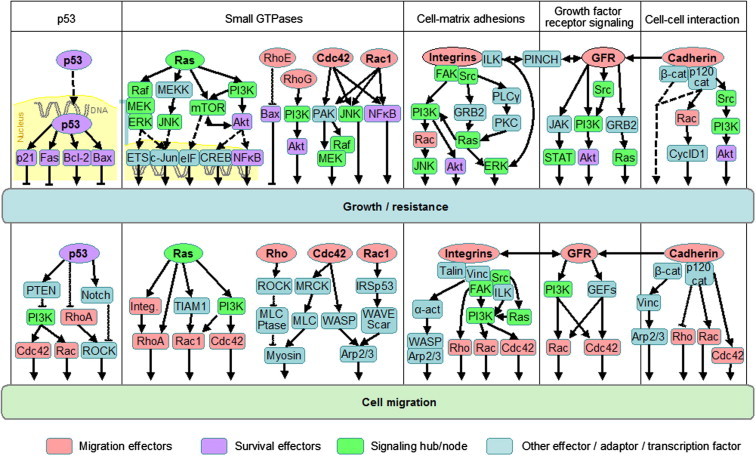
Signaling pathways controlling tumour cell growth, survival and invasion. Example pathways of p53, Ras GTPase, small Rho GTPases, integrins, growth factor receptors and cadherins with a dual role in controlling cell growth (upper row) and survival as well as cell migration and invasion (lower row). Migration effectors are marked in pink, survival effectors in purple, signaling hubs in bright green. Arrows indicate signaling direction. Bound to DNA, transcription factors. Figure taken from Ref. [3]. α-Act., α-actinin; cat, catenin; Cdc42, cell division cycle 42; CREB, cAMP response element-binding; CyclD1, cyclin D1; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; ERK, extracellular signal-related kinase; ETS, erythroblast transformation specific (transcription factor); FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GEF, guanine nucleotide exchange factor; GFR, growth factor receptor; GRB2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; ILK, integrin-linked kinase; Integ., integrin; JNK, Janus-kinase; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase; MEKK, MEK kinase; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; MLC, myosin light chain; MLCPtase, MLC phosphatase; MRCK, myotonic dystrophy kinase-related Cdc42-binding kinase; NFκB, nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhance’ of activated B cells; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PINCH, particularly interesting Cys–His-rich protein; PKC, protein kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase γ; PI3K, phosphoinosid-3-kinase; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homologue; ROCK, Rho-activated kinase; STAT, signal tranducer and activator of transcription; TIAM1, T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 1; Vinc, vinculin; WASP, Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome protein; WAVE; WASP family Verprolin-homologous protein. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
