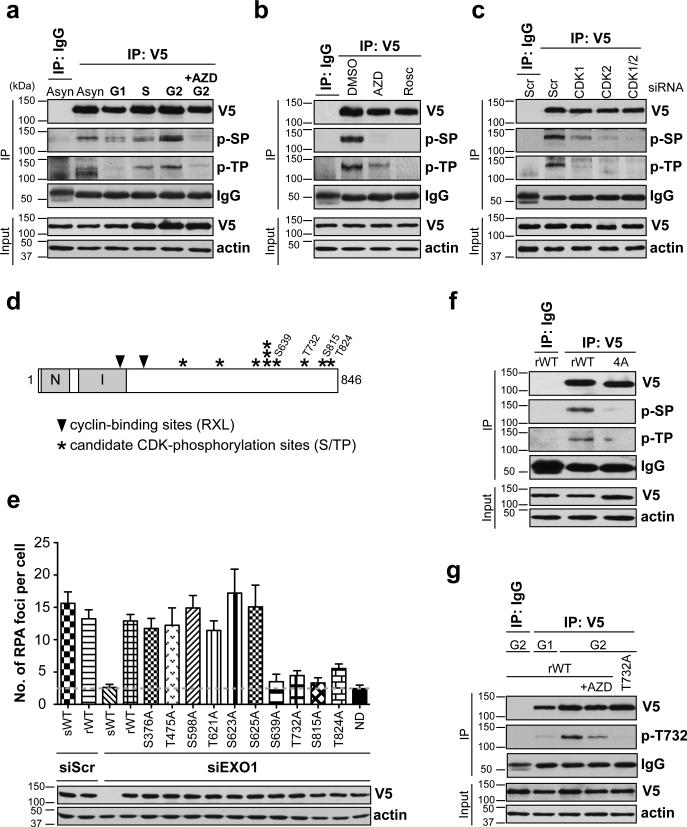
Figure 1. EXO1 is phosphorylated by CDKs 1 and 2 in S and G2 phases.
(a) HEK-293 cells expressing V5-EXO1 were synchronized in different phases of the cell cycle. EXO1 was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-V5 antibody and Western blotted with anti-phospho-Ser (p-SP) or anti-phospho-Thr (p-TP) CDK substrate antibodies, as indicated. “+AZD” indicates cells pre-treated with the CDK inhibitor AZD5438 prior to analysis. (b) HEK-293 cells expressing V5-EXO1, synchronized in G2, were pre-treated with CDK inhibitors, AZD5438 or Roscovitine, prior to analysis of EXO1 phosphorylation by IP-Western. (c) HEK-293 cells expressing V5-EXO1, with siRNA-mediated depletion of CDK1 and/or CDK2, were synchronized in G2 and EXO1 phosphorylation status determined by IP-Western. Scr denotes scrambled siRNA used as control. (d) Schematic of human EXO1 with asterisks indicating location of S/TP sites. Sites determined in this study to be important for resection are numbered. Locations of cyclin-binding (Cy) sites are indicated by solid triangles. N-terminal (N) and Internal (I) catalytic domains are indicated. (e) U2OS cells were depleted of endogenous EXO1 using siRNA and complemented with siRNA-resistant wild type EXO1 (rWT) or EXO1 individually mutated at S/TP sites, as indicated. Cells were screened for resection defects by quantifying IR-induced RPA foci. Average numbers of RPA foci per cell are plotted after subtracting background (average numbers of foci in mock-irradiated cells). Cells expressing siRNA-sensitive EXO1 (sWT) or siRNA-resistant nuclease dead EXO1 (ND) served as resection-defective controls (dashed line demarcates basal levels of RPA foci in these cells). Western blot shows comparable expression of EXO1 mutants and depletion of sWT-EXO1 by siRNA. (f) HEK-293 cells expressing WT-EXO1 or EXO1 with all four C-terminal S/TP sites mutated to Ala (4A-EXO1) were synchronized in G2, and EXO1 phosphorylation status determined by IP-Western. (g) HEK-293 cells expressing WT-EXO1 or EXO1 with a T732A point mutation were synchronized in G1 or G2, as indicated, and EXO1 phosphorylation at the T732 site was determined by IP-Western with anti-phospho-EXO1 (p-T732) antibody. All experiments were replicated three times. Error bars depict S.E.M. See also Supplementary Fig. 1.