Figure 7.
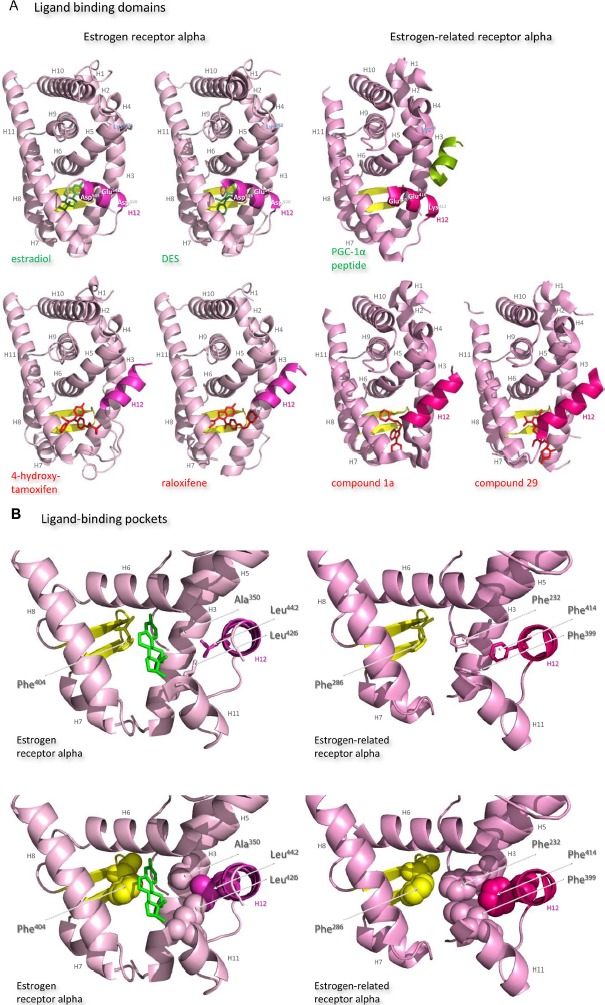
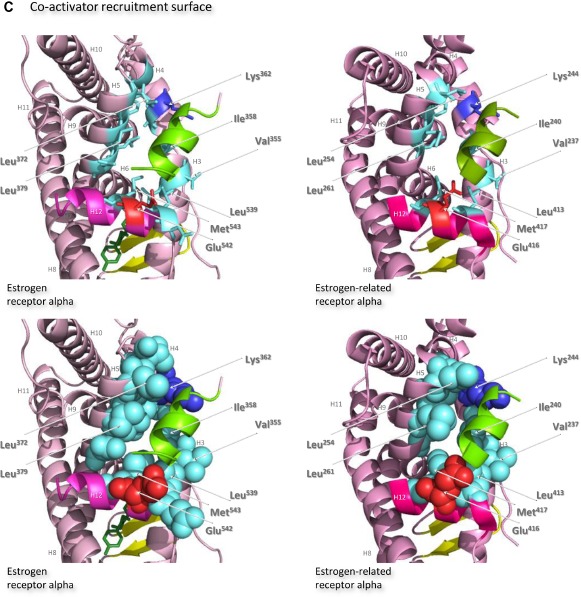
Structures of the ligand-binding domains of estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen-related receptor alpha in complex with their ligands.
Notes: Ribbon representations of the three-dimensional crystal structures of the ligand-binding domains of estrogen receptor alpha in complex with estradiol (a); DES (b); 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen, a high-affinity metabolite of tamoxifen (c); and raloxifene (d), and of estrogen-related receptor alpha in complex with a PGC-1α peptide (e); compound 1a (f); and compound 29 (g) (A). Helices 1–11 of estrogen receptor alpha are colored pale pink and those of estrogen-related receptor alpha pink. The 12th helices are colored darker shades of pink and the short antiparallel beta sheets are colored yellow. The ligands, shown in stick view, and coactivator peptides, shown in a ribbon representation, are colored green if they increase activity of the receptor and red if they inhibit its activity. The helices are numbered and the four charged residues proposed initially to be critical for coregulator interaction are labeled. Ribbon representations of the ligand-binding pockets of estrogen receptor alpha in complex with estradiol and of estrogen-related receptor alpha in complex with a PGC-1α peptide are shown with estradiol shown in stick representation (B). The molecules are rotated to the right compared to the views shown in (A), with helix 11 to the front and helix 12 to the right of the structures. Much of helix 11 has been removed to allow better visualization of the occupancy of the ligand-binding pockets. The side chains of the four phenylalanine residues, Phe232, Phe286, Phe399, and Phe414, that are orientated towards the ligand-binding pocket of estrogen-related receptor alpha and are thought to contribute to stabilization of its active conformation, and the equivalent residues of estrogen receptor alpha, Ala350, Phe404, Leu426, and Leu442, are indicated and labeled, and their side chains are shown in stick representation (top) or in space-filling mode (bottom). Helices are numbered and colored as in (A). Ribbon representations of the coactivator recruitment surfaces of estrogen receptor alpha in complex with DES and a GRIP1 peptide, and of estrogen-related receptor alpha in complex with a PGC-1α peptide, are shown (C). The molecules are rotated slightly to the left compared to the views shown in (A) to allow better visualization of the hydrophobic cleft formed between helices 3, 4, 5, and 12. The helices are numbered and colored as in (A). The residues involved in the coactivator peptide interaction are shown in stick representation (top) and space-filling representation (bottom). Most have hydrophobic side chains and are colored light blue. The charged Lys and Glu residues that form charged capping interactions at either end of the coactivator peptide are colored blue and red, respectively. Conserved residues that were identified as being involved in interactions with the coactivator peptides in both structures and that are clearly visible in the figure are indicated. All images were created with PyMol Molecular Graphics Software (Schrödinger, Portland, OR, USA).
Abbreviations: DES, diethylstilbestrol; PGC, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator.
