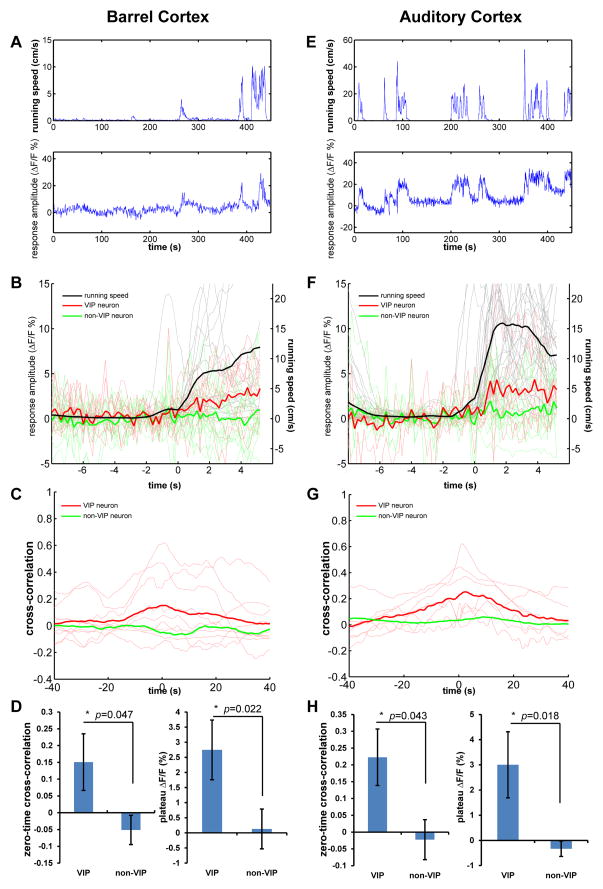
Figure 7.
Locomotion activates VIP neurons in primary somatosensory and auditory cortices.
(A) Example showing calcium response of a VIP neuron in barrel cortex in relation to running speed. (B) The calcium response of VIP (red traces, n=9, 3 mice) and non-VIP neurons (green traces, n=15, 3mice) in barrel cortex aligned to the running episodes (black traces). Each thin trace (red or green) is the average of all extracted responses of a single cell. (C) Cross-correlation between calcium responses and running speed. Thin red lines show cross-correlation curves of all recorded VIP neurons. The thick red curve is the average of all thin red curves. The thick green curve is the average of the cross-correlation curves of all recorded non-VIP neurons. (D) The average zero-time cross-correlation of VIP neurons is significantly different from that of non-VIP neurons (left panel, Mann-Whitney U-test). The average plateau amplitude of running-aligned calcium responses is significantly different from that of non-VIP neurons (Mann-Whitney U-test). (E–H) Corresponding data for auditory cortex.