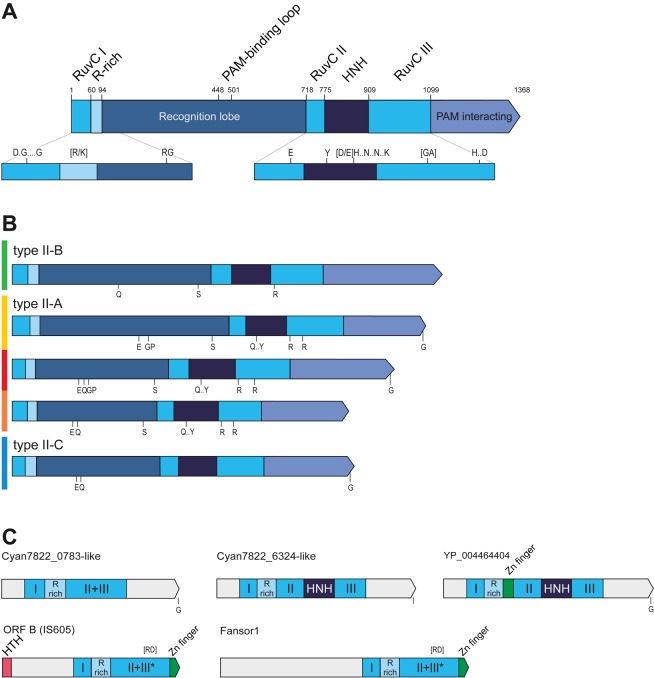
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of Cas9 domain organization, motifs and relationships with distant homologs. (A) A general view of the domain architecture of Cas9. (B) Comparison of the domain organizations and conserved sequences motifs between the major groups of Cas9 proteins. (C) Domain architectures of distant homologs of Cas9. Homologous regions are shown by the same color. Compare with Supplementary Figure S8. The S. pyogenes Cas9 schematic representation with domains and domain boundaries according to the Cas9 structures (76,77) is shown in (A). See Supplementary Figure S4. Distinct sequence motifs are denoted by the corresponding conserved amino acid residues. The residues indicated in (A) are conserved in all five Cas9 groups and in (B), within the given subtype. Compare with Supplementary Figure S4. The size of a domain or a distinct region is roughly proportional to the length and the motifs are shown in accordance with their approximate position within a respective protein. The scheme was derived from the multiple alignments of each group. The color code to the left of the protein schematics in (B) corresponds to the major branches of the Cas9 phylogenetic tree in Figure 4. HTH: helix turn helix DNA-binding domain; R-rich: arginine-rich region; HNH: nuclease of the corresponding family.