Figure 1.
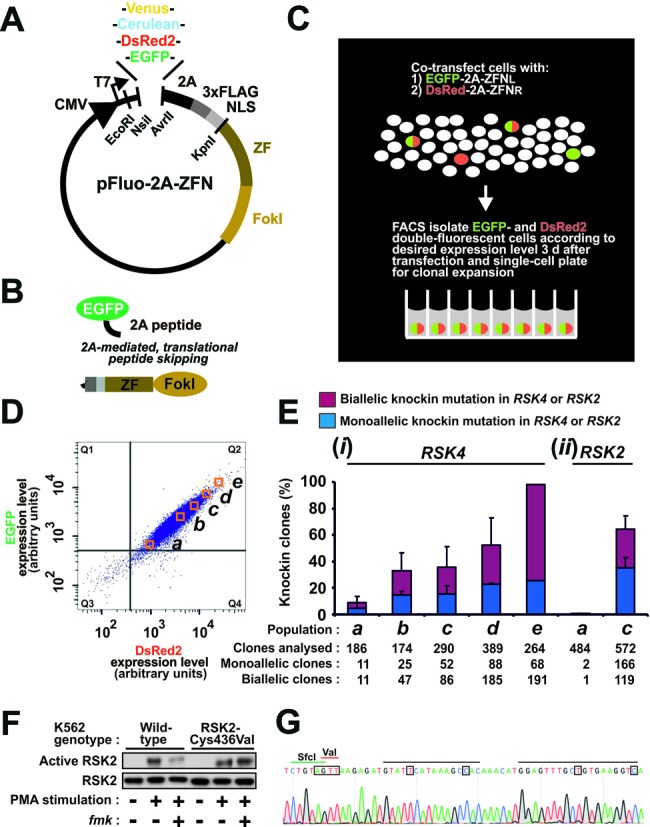
High-efficiency genome editing via 2A-coupled co-expression of ZFNs and fluorescent proteins combined with FACS. (A) Schematic of the pFluo-2A-ZFN construct for 2A-coupled, 1:1 co-expression of ZFN and fluorescent protein. Functional parts indicated are CMV promotor, fluorescent protein (Venus, Cerulean, DsRed2, EGFP), 2A peptide, triple FLAG epitope tag, nuclear localization signal (NLS), zinc finger (ZF) moiety and FokI nuclease moiety. The restriction endonuclease sites NsiI/AvrII and EcoRI/KpnI can be used to swap fluorescent protein and ZFN, respectively. (B) Fluorescent protein and ZFN expressed from Fluo-2A-ZFN transcripts are co-expressed as separate entities due to translational skipping at the 2A sequence. (C) Overview of strategy for high-efficiency genome editing via FACS isolation of cells that co-express fluorescent protein and ZFNs. In this example, left and right ZFNs of a pair (ZFNL and ZFNR) have been coupled to distinct fluorescent proteins. (D) FACS profile of K562 cells 3 days after transfection with mRNA for EGFP-2A-ZFNL and DsRed2–2A-ZFNR targeting the RSK4 locus along with an ssODN knockin donor (RSK4 Cys443Val/BamHI). Cells from populations displaying low to high EGFP/DsRed2 double-fluorescence intensities (a)–(e) were FACS isolated and single-cell seeded for clonal expansion. Cells in the gate Q3 have fluorescence intensities similar to mock-transfected cells. (E) Frequency of monoallelic and biallelic knockin modification at (i) the diploid RSK4 locus in clonal cell lines derived from populations (a)–(e) or at (ii) the diploid RSK2 locus in a similar knockin experiment using reagents for RSK2 and analysing populations (a) and (c) only. Except for population (e) that was isolated only once, the data are means + SD of three independent experiments. (F) Functional codon conversion at the RSK2 locus. Wild-type or clonal K562 cells with biallelic Cys436Val knockin modification of RSK2 derived from (c) in panel (E) were analysed for sensitivity of RSK2 to fmk by immunoblot analysis after exposure of cells to the stimulus PMA in the absence or presence of fmk. The data are representative of those obtained with five clones analysed. (G) Genomic sequence of an RSK2 Cys436Val clone, indicating the ZFN-binding sites (black bars), the Val436 codon (red bar) and the diagnostic SfcI site (green bar). The mutations introduced are boxed. Those occurring in the ZFN target site aimed to prevent re-cutting of the locus once the donor had been knocked in.
