Figure 2.
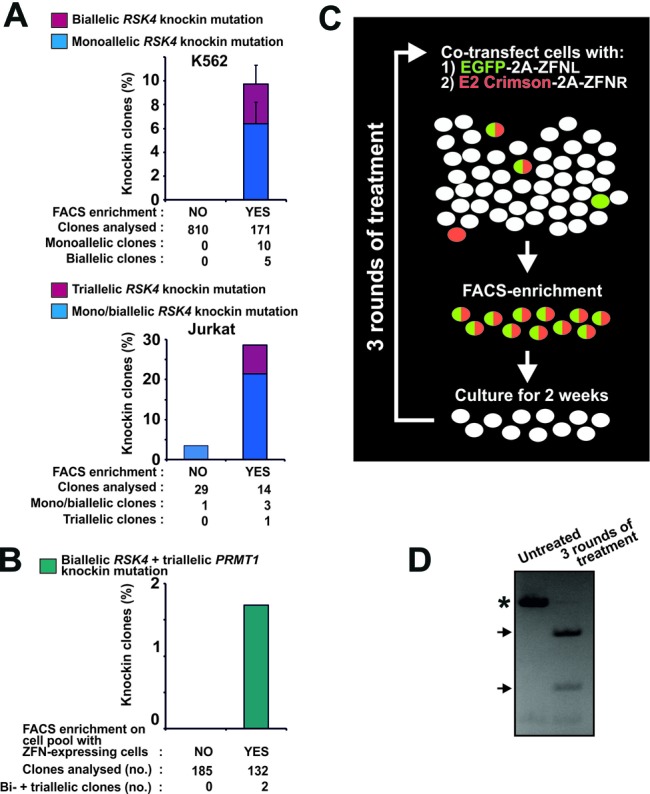
Fluorescent protein-2A-ZFN constructs enable efficient knockin genome editing in demanding applications. (A) K562 or Jurkat cells were transfected with mRNA expressing EGFP-2A-ZFNL and DsRed2–2A-ZFNR for RSK4 along with an ssODN knockin donor (RSK4 Cys443Val/BamHI). For K562, the cells were diluted 3 days post-transfection with mock-transfected cells to produce a pool of ∼0.5% ZFN-expressing cells. Cells of this pool were seeded singly or subjected to FACS isolation of EGFP/DsRed2 double-fluorescent cells (any level) that were thereafter also seeded singly. For Jurkat, non-sorted cells or cells FACS isolated from the 15% most highly EGFP/DsRed2 double-fluorescent cell population were seeded singly 3 days post-transfection. In both experiments, the singly seeded cells were expanded to clonal cell lines and analysed for knockin mutation by RFLP analysis. For K562, data are means + range of two independent experiments. (B) K562 cells were co-transfected with mRNA expressing EGFP-2A-ZFNs (left and right) for RSK4 and DsRed2–2A-ZFNs (left and right) for PRMT1 along with ssODN donors for knockin modification of these loci (RSK4 Cys443Val/BamHI and PRMT1 ScaI). Three days after transfection, non-sorted cells or cells FACS isolated from the 15% most highly EGFP/DsRed2 double-fluorescent cell population were seeded singly, expanded to clonal cell lines and analysed for complete knockin modification of the RSK4 and PRMT1 loci. Data are summed of three independent experiments. (C) Overview of strategy for generation of cell pools with high levels of stable knockin modification. In this case, left and right ZFNs of a ZFN pair (ZFNL and ZFNR) have been coupled to distinct fluorescent proteins. (D) Example of close to 100% knockin in an MCF10A cell pool. Specifically, MCF10A cells were transfected for codon-conversion knockin at the RSK2 locus as described in Figure 1E, (ii). Three days after transfection, the 40% most highly fluorescent cells were FACS isolated and cultured as a pool for 2 weeks. Thereafter, this cell pool was subjected to the same treatment for two more rounds. After the third round, the cell pool was analysed for stable knockin at the RSK2 locus by RFLP analysis with untreated MCF10A cells serving as a control. PCR products derived from wild-type and mutant alleles are indicated by an asterisk and arrows, respectively.
