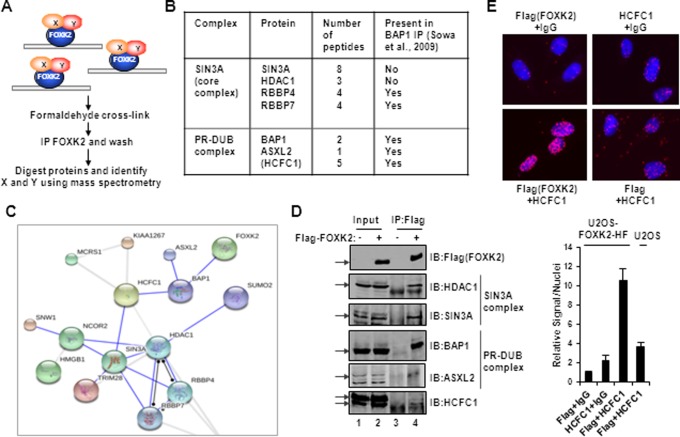
Figure 1.
Identification of FOXK2 binding proteins by RIME. (A) Schematic illustration of the RIME protocol used to identify FOXK2 associated factors in the context of chromatin association. (B) Summary of FOXK2 interaction proteins belong to the SIN3A core complex and the PR-DUB complex. HCFC1 is shown in brackets as it is unclear whether this is part of the core PR-DUB complex. (C) Visualization using STRING of a sub-network of interactions between FOXK2 binding proteins. (D) Validation of FOXK2 interaction with endogenous components of SIN3A and PR-DUB core complex proteins by co-immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments using anti-Flag (FOXK2) antibody in U2OS–FOXK2–HF cells. Precipitated proteins were detected by immunoblotting (IB) using the antibodies as indicated. Arrows represent the bands corresponding to each of the full-length proteins. Note that the ASXL2 blot is from a different IP experiment. (E) PLA analysis of interaction between Flag-tagged FOXK2 and endogenous HCFC1 in U2OS–FOXK2–HF (top and bottom left panels) or U2OS (bottom right) cells. The combinations of antibodies used are shown above and below each panel (IgG represents a non-specific antibody). DNA is stained using DAPI (blue) and the PLA signal is red. Quantitative analysis of PLA signals in the nucleus is shown below. The level of signals/nuclei in the control PLA sample (Flag and non-specific IgG antibodies) was set as 1.