Figure 6.
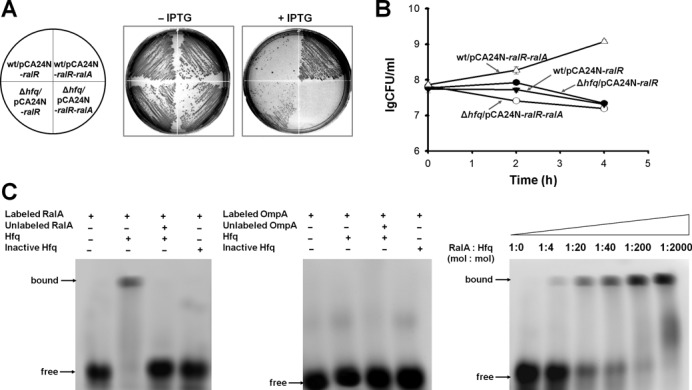
Hfq is required for RalA antitoxin activity. (A) Cell growth on LB plates supplemented with chloramphenicol (30 μg/ml) with and without 0.5 mM IPTG for cells producing RalR and RalR/RalA in the wild-type host and in the Δhfq host, respectively. (B) CFU test over time for cells producing RalR and RalR/RalA in the wild-type host and in the Δhfq host, respectively. Overnight cultures were diluted to OD600 0.1, and 1 mM IPTG was added initially. This assay was performed twice with two independent cultures, and one standard deviation is shown. (C) EMSA shows that Hfq binds to RalA sRNA (left panel) but not to the 3′ end of the coding region of ompA mRNA (middle panel). The binding of Hfq to RalA increases with increasing Hfq (right panel).
