Figure 5.
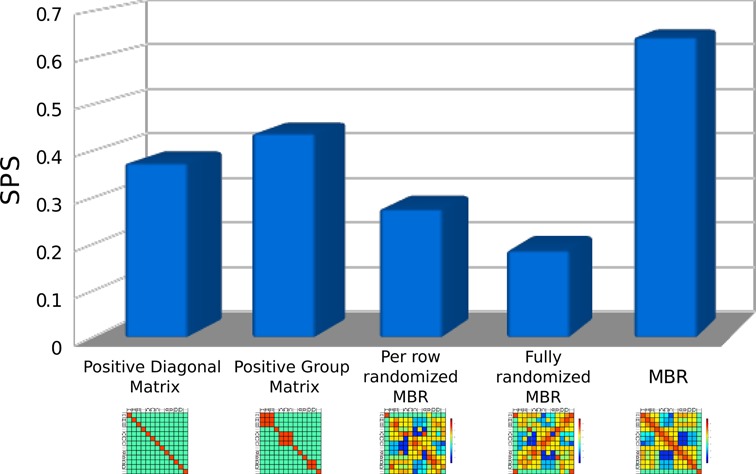
Alignment performances using different types of matrices. The MBR and four other different matrices are used to align the structures of pairs of RNAs sampled from Rfam using an implementation of the Needleman–Wunsch algorithm able to receive as input the BEAR encoding. ‘Positive diagonal’ is a matrix where a positive score is assigned to identical characters, and a negative score everywhere else. ‘Positive group’ is a matrix where a positive score is assigned between elements of the same type of RNA SS, and a negative one everywhere else. ‘Per row randomized MBR’ and ‘Fully randomized MBR’ are matrices built using randomized values of the MBR. More details can be found in the main text. The fifth column shows the performance of the MBR matrix, without the sequence BONUS. Sum-of-pairs (SPS), which is the fraction of correctly aligned nucleotide pairs, is used as quality measure.
