Figure 3.
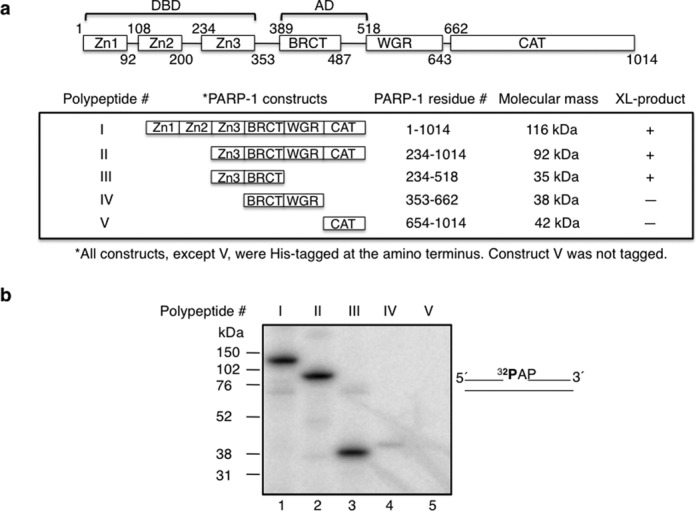
Cross-linking of various PARP-1 domain constructs to AP site-containing DNA. (a) Schematic representation of human PARP-1 sub-domains. Zn1, Zn2, Zn3, BRCT, WGR, and CAT represent, zinc finger 1, zinc finger 2, zinc finger 3, BRCA C-terminus, tryp-gly-arg-rich region, and carboxy-terminal catalytic sub-domains of PARP-1, respectively. PARP-1 residues of each construct are indicated. BRCT is located within the region of AD of PARP-1. DBD consists of Zn1, Zn2 and Zn3 sub-domains of PARP-1. Various PARP-1 polypeptides (I–V) representing full-length PARP-1, Zn3-CAT, Zn3-BRCT, BRCT-WGR, and CAT, respectively, were expressed in E. coli and purified to near homogeneity as described under Materials and Methods. The residue numbers of each construct and the relative molecular mass (kDa) of each construct are indicated. All the constructs were His-tagged at the amino terminus, except CAT sub-domain that has no tag. The intrinsic cross-linking reactivity to AP-DNA is indicated by positive (+) or negative (-) sign. (b) Intrinsic cross-linking of purified PARP-1 polypeptides (I–V) to AP site-containing DNA. 5′-end 32P-labeled 34 bp DNA with an AP site in a nick (i.e. 5′-dRP), shown next to the phosphorimage, was used for cross-linking. PARP-1 polypeptide (I–V) and 32P-labeled DNA were incubated on ice without NaBH4 as in Figure 1(a). The cross-linking products were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and followed by phosphorimaging. The relative positions of marker proteins are indicated.
