Figure 5.
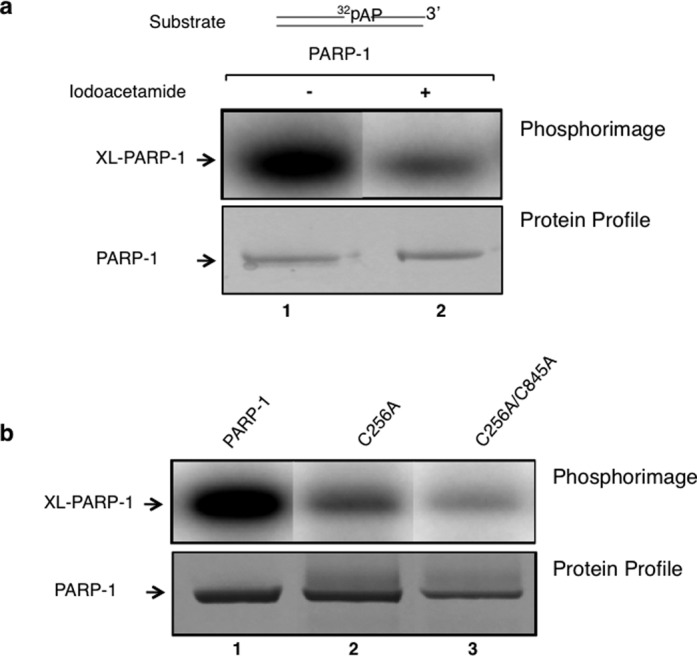
Site-directed alterations and iodoacetamide treatment of PARP-1 reduce intrinsic covalent cross-linking of PARP-1. (a) A phosphorimage of cross-linked PARP-1 to 32P-labeled AP site-containing DNA is shown. PARP-1 (10 μM) was incubated with 50 mM iodoacetamide in a reaction mixture (10 μl) containing 25 mM NaPO4 buffer, pH 7.0 and 25 mM NaCl for 30 min at room temperature in the dark. Then, the addition of 60 mM DTT was used to terminate the reaction. The excess amounts of iodoacetamide and DTT were removed with a Zebra micro spin desalting column. The intrinsic cross-linking reaction was performed with untreated PARP-1 (lane 1) or iodoacetamide-treated PARP-1 (lane 2). After capturing the phosphorimage of the 32P-labeled DNA-PARP-1 complex (upper panel), the same gel was stained with Coomassie-blue for proteins (lower panel). (b) Photographs of the phosphorimage and the Coomassie-stained gel are shown. The cross-linking reaction was performed with wild-type (lane 1), single mutant C256A (lane 2) or with a double mutant C256A/C845A (lane 3) of PARP-1 as in panel (a). The results revealed a significant reduction in cross-linking of PARP-1 with the iodoactamide-treated sample or with the alteration of solvent exposed cysteine residues 256 and 845 to alanines.
