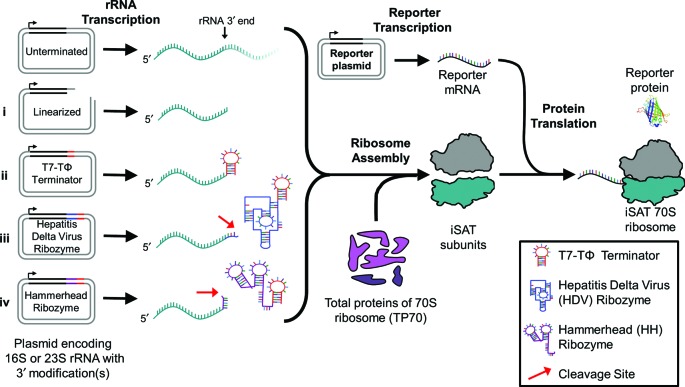
Figure 1.
Integrated 16S and 23S rRNA synthesis, 70S ribosome assembly, and reporter protein translation (iSAT) using rRNA constructs containing 3′ gene modifications. rRNA are transcribed from plasmids by T7 RNA polymerase and assembled with purified total protein of the 70S ribosome (TP70) into 70S iSAT ribosomes. Newly assembled ribosomes translate co-transcribed mRNA encoding the reporter proteins luciferase or sfGFP. These steps occur simultaneously at 37°C, and active luciferase or sfGFP synthesis is used as a measure of ribosome activity. ‘Unterminated’ refers to the use of plasmids pWK1 and pCW1 encoding 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA, respectively, as previously reported (11). Modifications to the 3′ ends of the rRNA genes include (i) 3′ linearization by digestion with the restriction enzyme Bsu36I (pWK1) or Aflll (pCW1) to allow for run-off transcription, or addition of (ii) T7-TΦ terminators, (iii) hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozymes or (iv) hammerhead (HH) ribozymes. Ribozymes are expected to self-cleave, denoted by red arrows, to minimize the number of additional bases included beyond native 16S or 23S rRNA 3′ ends. T7 terminators are included after ribozyme genes to limit excess transcription.