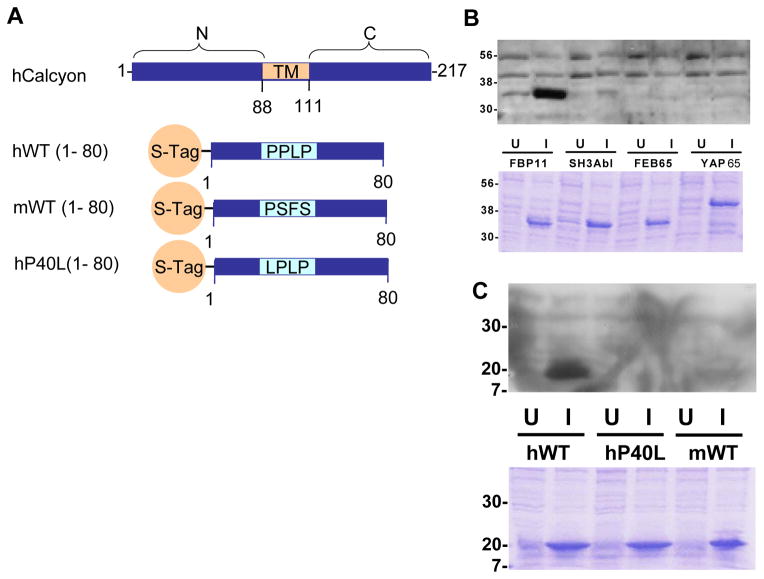
Figure 5.
The primate PPLP motif mediates interaction of calcyon with WW domain proteins. A. Diagram of the transmembrane (TM) domain structure of calcyon. The N-terminal 80 residues of murine calcyon and both the P40 and L40 variants of hCalcyon were fused to the STag for ‘overlay’ assays shown in B and C. B. Binding specificity of the calcyon WW domain. Bacteria were transformed with pGEX expressing GST fusion proteins of the indicated WW domains (FBP11, FEB65, and YAP65), or the SH3 domain of Abl. Fusion proteins were induced with isopropyl β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG). Uninduced (U) and induced (I) bacterial extracts were separated on an SDS-PAGE gel, stained with coomassie blue (lower panel) or transferred to PVDF membrane (upper panel). After blocking, blots were incubated with 1 mg purified S-hWT (1-80) in blocking buffer overnight. Binding of S-Tag-hWT (1-80) was detected with anti-S protein conjugated to HRP, followed by ECL and exposure to autoradiography film. C. The FBP11 WW domain binds the calcyon hWT(P40), but not to either the murine or hP40L S-Tag fusion proteins. Overlay assay performed by incubating purified GST-FPB11 with a blot of uninduced and induced lysates of bacteria transformed with the indicated calcyon S-Tag fusion proteins. Bound GST-FBP11 was detected with HRP conjugated anti-GST antibodies as in B. For both B and C, similar results were obtained in at least two independent experiments.