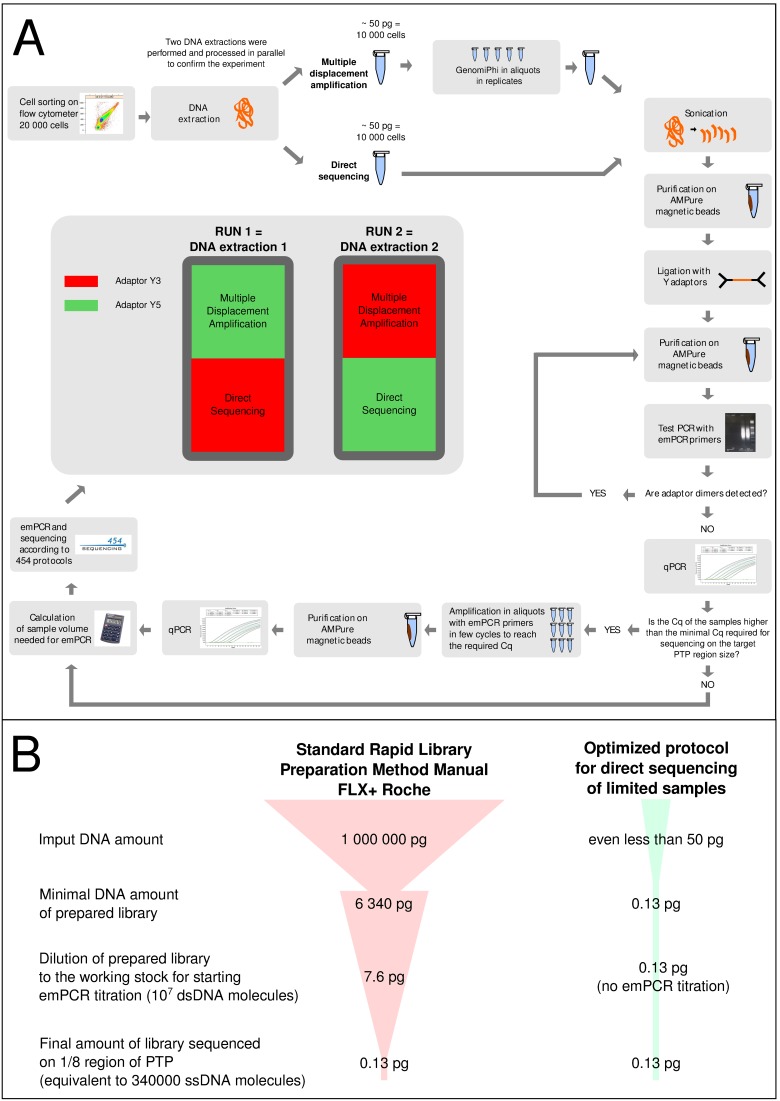
Figure 1. Flowchart of the minimal library preparation protocol.
Panel A: The experimental work started with cell sorting, where 20,000 cells were separated in two replicates to confirm the whole experiment. The DNA from 20,000 cells was extracted and split into halves, where one half was amplified with GenomiPhi (MDA) and a second half was processed without whole genome amplification (DS). The shotgun libraries were prepared with the same alternative protocol for the both MDA and DSsamples. Library quality control points were the test PCR with emPCR primers to prove the removal of self-ligated adaptors and the library concentration checking with qPCR. The MDAsample and DSsample with different MIDs in two repetitions were combined into two sequencing runs as sho! wn in the scheme. Panel B: DNA amount requirements in the standard Rapid Library Preparation Method Manual GS FLX+ Series – XL+ (May 2011) compared with the amounts actually needed for sequencing on a selected PTP region. The minimal amount of prepared library required for proceeding to emPCR step in the standard 454 protocol may lose 99% of input DNA during the library preparation step. Then, this amount is diluted to a working stock of 10–7 molecules, defined as the best starting point to perform the emPCR titration step. However, if the exact number of molecules is quantified with qPCR, the emPCR titration step can be omitted, so actually only 0.13 pg of prepared library are needed for sequencing on 1/8 region of PTP (equivalent to 340,000 ssDNA molecules). This allows to use an alternative shotgun protocol where the DNA losses are reduced.