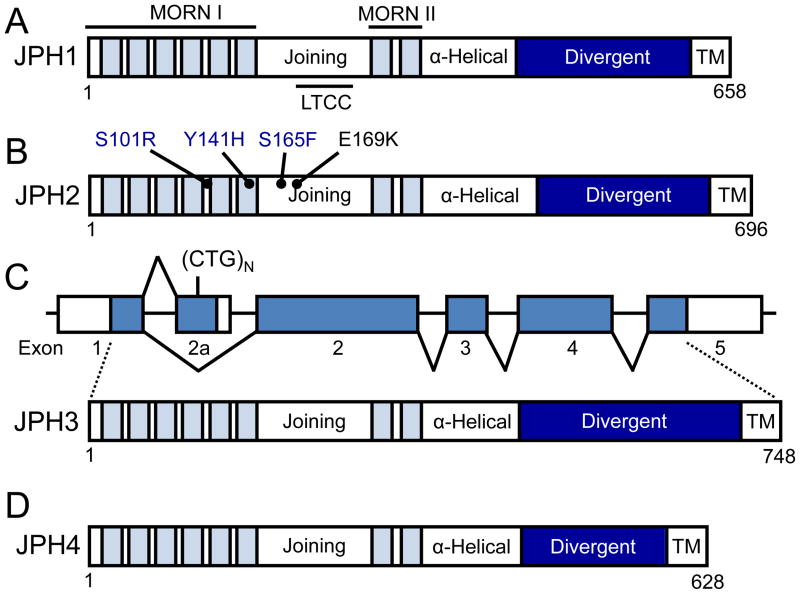
Figure 1. Protein topology of the four junctophilin isoforms expressed in humans.
The JPH amino terminus has 8 MORN motifs (light blue fill) distributed across two MORN domains separated by a joining region (white fill). The carboxy terminus contains a transmembrane (TM) domain (white fill) which embeds this end of the protein into intracellular membranes such as the sarcoplasmic reticulum in striated muscle. An alpha-helical domain (white fill) and a less evolutionarily conserved divergent region (dark blue fill) join these two termini. The isoforms vary in length from 628 (JPH4) to 758 (JPH3) residues. (A) Protein topology of JPH1, which is found predominantly in skeletal muscle. JPH1 binds to the LTCC via a binding domain within the joining region of the protein. (B) Protein topology of JPH2, the major cardiac isoform. Three JPH2 mutations have been linked with the development of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (blue text) and one to arrhythmogenesis (black text). (C) Schematic of the two alternatively spliced transcripts of JPH3 including the untranslated regions (white fill) and coding exons (blue fill). The full length transcript consisting of 5 exons which encode JPH3 is depicted as well as the 2 exon alternative transcript containing the CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion in the alternate exon 2 (2a). Below is the protein topology of JPH3. (D) Protein topology of JPH4. Abbreviations: JPH, junctophilin; LTCC, L-type calcium channel binding domain; MORN, membrane occupation and recognition nexi; TM, transmembrane domain.