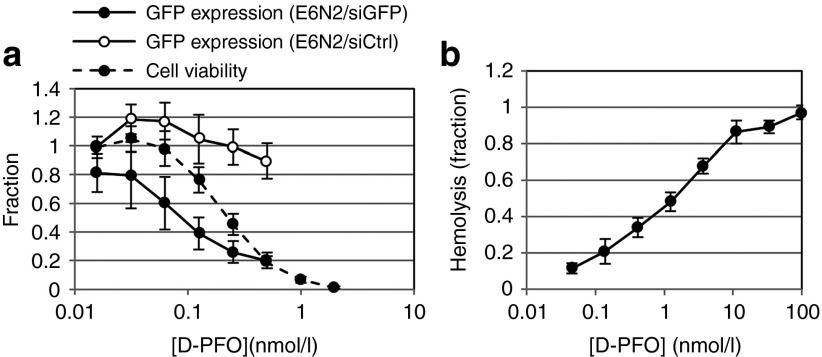
Figure 3.
Characterization of D-PFO fusion protein for endosomal escape. (a) GFP knockdown assays were performed in A431-d2EGFP cells, along with cell viability measurements to obtain a therapeutic window. E6N2 was used to deliver 100 nmol/l of either gfp siRNA (siGFP) or control siRNA (siCtrl) to A431-d2EGFP cells with varying amounts of D-PFO. The therapeutic window of D-PFO is shown with cell viability overlaid with GFP expression (data shown as mean ± SD, n = 9). Viability is normalized to a value of 1 for untreated cells and 0 for wells without cells. GFP expression is normalized to a value of 1 for untreated A431-d2EGFP cells and 0 for A431 cells. (b) The membrane disruptive activity of PFO is measured in a mouse red blood cell hemolysis assay. Hemolysis is normalized to 1 for 10% Triton-X 100–treated cells and 0 for untreated cells (data shown as mean ± SD, n = 3). siRNA, short-interfering RNA.