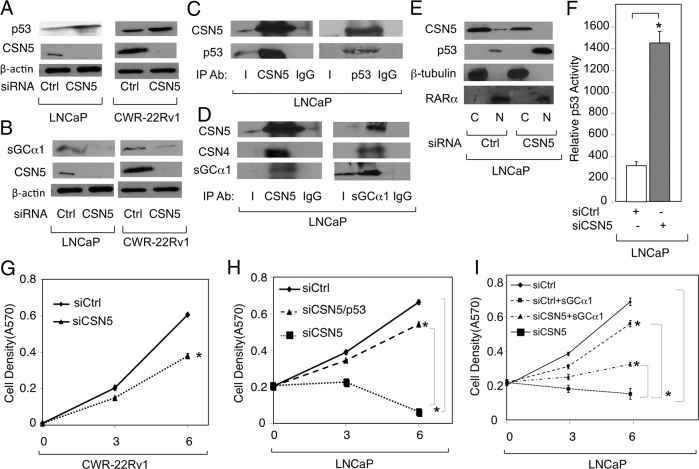
Figure 7.
CSN5 antagonistically regulates p53 and sGCα1 proteins in prostate cancer. LNCaP and CWR-22Rv1 cells were transfected with Ctrl siRNA or CSN5 siRNA, and Western blotting was used to measure (A) CSN5 and p53, (B) CSN5 and sGCα1, (E) CSN5 and p53 in cytosolic (C) or nuclear (N) fractions, or (F) p53 transcriptional activity using a luciferase assay. β-Actin was used as loading control and the molecular weights of the proteins are 53 kDa (p53), 38 kDa (CSN5), 49 kDa (CSN4), 42 kDa (β-actin), 50 kDa (β-tubulin), and 52 kDa (retinoic acid receptor-α). β-Tubulin and retinoic acid receptor-α were used as markers for cytosolic and nuclear fractions, respectively. LNCaP cell extracts were subjected to IP using antibody against (C) CSN5 or p53 or (D) CSN5 or sGCα1. IgG was used as negative control IP. Western blotting was used to measure CSN5, p53, and sGCα1. CWR-22Rv1 and LNCaP cells were transfected with (G) Ctrl siRNA or CSN5 siRNA, (H) Ctrl siRNA or CSN4 siRNA, with or without p53 siRNA, or (I) Ctrl siRNA or CSN5 siRNA, with or without sGCα1 expression plasmid. Cell density was measured by mammalian transient transfection (MTT) assay. In panels F, G, H, and I, data points represents an average of 3 independent experiments plus SDs. Asterisks indicate statistical significance (P < .004) in panel F and (P < .03) in panels G, H, and I. Student's t test was used to analyze the data. Ab, antibody.