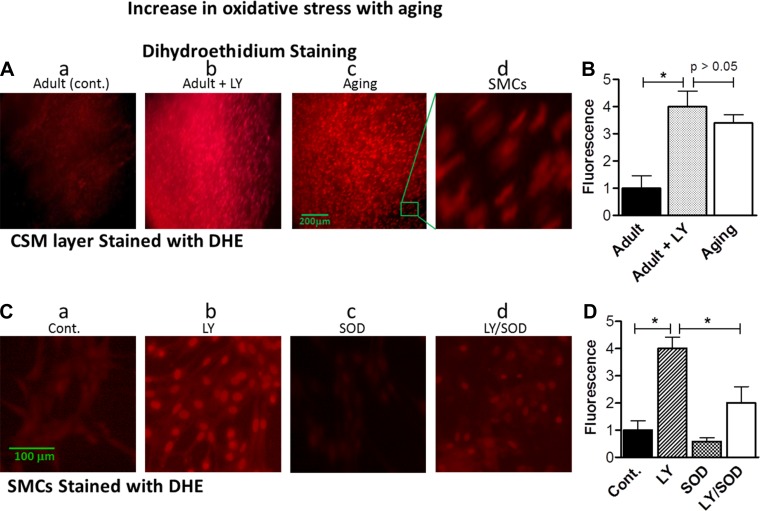
Fig. 3.
A: immunofluorescent images of dihydroethidium (DHE)-stained IAS circular smooth muscle (CSM) layer from adult and aging rats. B: quantitative data from images in A. LY83583 (LY) causes a significant increase in oxidative stress in the adult rats, comparable to that in aging rats. Values are means ± SE of 4 animals. *P < 0.05. C: immunofluorescent images of IAS smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from adult rats. D: quantitative data from images in C. Pretreatment with LY83583 caused a significant increase in oxidative stress that was significantly attenuated by pretreatment with 200 U/ml SOD. Changes in O2·− (as a measure of oxidative stress) were monitored by DHE fluorescence, which shows an increase in O2·− by LY83583 and during aging and attenuation of O2·− by SOD (reflecting a decrease in oxidative stress by conversion of O2·− to H2O2). Cont, control. Values are means ± SE of 4 animals. *P < 0.05.