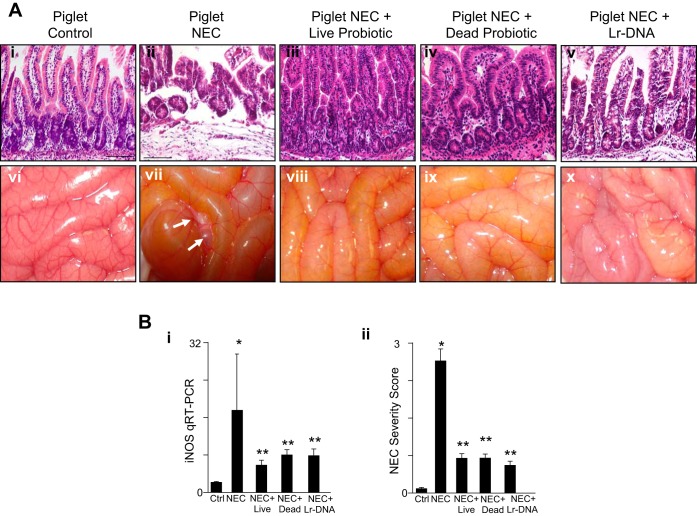
Fig. 4.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates the severity of experimental NEC in premature piglets. A: representative photomicrographs of the terminal ileum (i–v) and gross images of the intestines (vi–x) of premature piglets that were either untreated and euthanized at birth (controls) or induced to develop experimental NEC in the absence or presence of live or UV-irradiated (dead) probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 or Lr-DNA. Arrows show areas of pneumatosis intestinalis. B: NEC severity in the premature piglets as assessed by iNOS expression by qRT-PCR in the terminal ileum (i) or NEC severity score as determined by a pathologist blinded to the groups (ii). In all graphs, *P < 0.05 NEC vs. control; **P < 0.05 NEC vs. NEC + treatments with the live, UV-irradiated (dead) or the Lr-DNA. Data are means ± SE. Size bar = 50 μm. Combined data from 3 separate experiments in which piglets had been randomly assigned to each group: Ctrl, n = 4; NEC, n = 7; NEC + live probiotic, n = 4; NEC + dead probiotic, n = 3; NEC + DNA, n = 3.