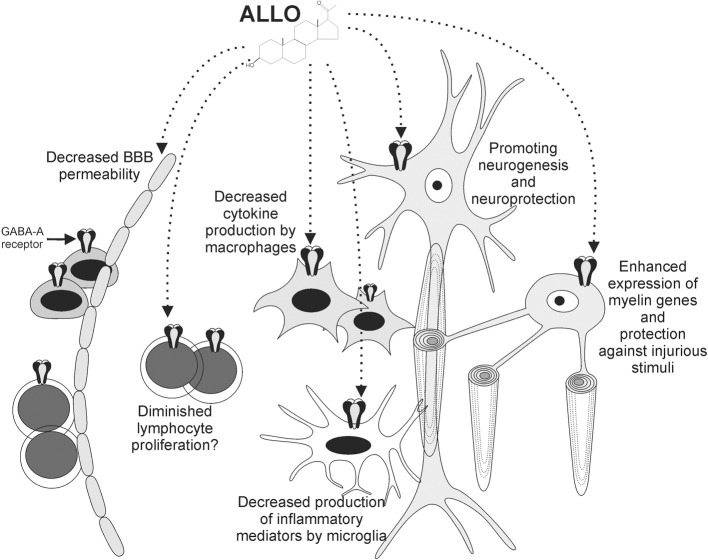
Figure 1.
ALLO exerts various effects on cells involved in MS pathogenesis. Functional GABA-A receptors are expressed by neurons, oligodendrocytes, monocytoid cells, and lymphocytes. ALLO promotes myelin gene expression by oligodendrocytes and protects them against injurious stimuli. Neuroprotective effects have also been reported for neurons. ALLO's binding to GABA-A receptors on monocytoid cells leads to diminished production of inflammatory mediators by these cells. These effects, together with diminished BBB permeability and potential influence on lymphocytes, contribute to the beneficial roles of ALLO in the context of autoimmune demyelination.