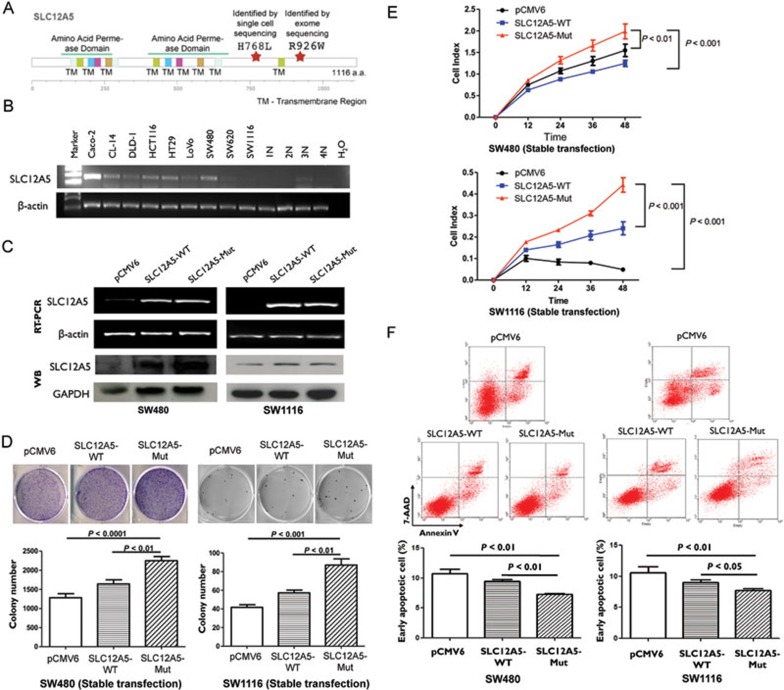
Figure 6.
Oncogenic function of SLC12A5 H768L mutant. (A) A schematic view of the domain structure of SLC12A5 and the site of point mutation (H768L) detected by single-cell sequencing. Another mutation site R926W detected by whole-tissue exome sequencing in 1 out of 21 cases of colon cancer was also illustrated. (B) The overexpression of SLC12A5 mRNA in colon cancer cell lines compared with normal colonic tissues (1N-4N) was demonstrated by RT-PCR. (C) Ectopic expression of SLC12A5 in colon cancer cell lines SW480 and SW1116 stably transfected with pCMV6 (vector), wild-type pCMV6-SCL12A5 (WT) and pCMV6-SLC12A5 H768L (Mut) was evidenced by RT-PCR and western blot. (D) The effect of stable overexpression of wild-type or mutant SLC12A5 on cancer cell proliferation was determined by colony formation assay. Mutant SLC12A5 significantly enhanced clonogenicity in SW480 (left) and SW1116 (right) cells compared with the wild-type SLC12A5 and empty vector control. (E) The effect of stable expression of wild-type or mutant SLC12A5 on colon cancer cell proliferation was determined by the xCELLigence System. SLC12A5 H768L mutant significantly promoted cell proliferation in SW480 and SW1116 cells compared with the wild-type SLC12A5 and empty vector control. (F) Annexin V/7-AAD analysis by flow cytometry revealed that overexpression of mutant SLC12A5 significantly reduced basal levels of early apoptotic cells in SW480 and SW1116. Data are means ± SD of three separate experiments in triplicates.