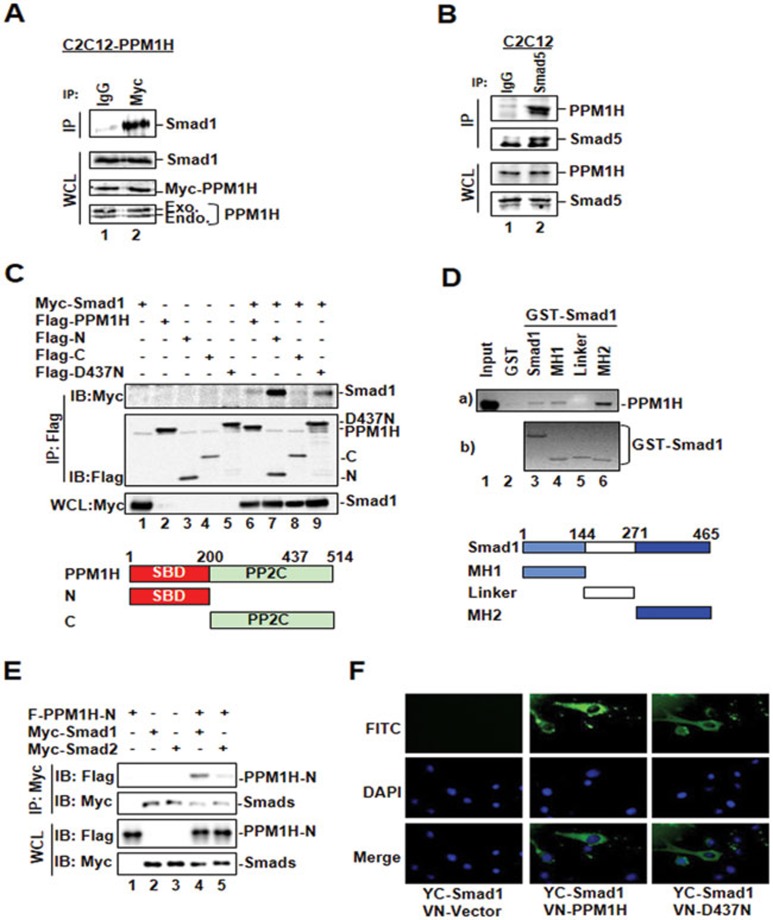
Figure 2.
PPM1H physically interacts with Smad1. (A) PPM1H co-immunoprecipitates with Smad1. C2C12 cells stably expressing Myc-PPM1H were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP)27 with anti-Myc antibody, and PPM1H-bound endogenous Smad1 was detected by western blotting with anti-Smad1 antibody. Mouse lgG was used for control IP (lane 1). (B) PPM1H binds to Smad5 at endogenous levels. C2C12 cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Smad5 antibody. Smad5-bound PPM1H was detected by western blotting with anti-PPM1H antibody. Rabbit lgG was used for control IP (lane 1). (C) The N-terminal region of PPM1H is the Smad1-binding domain. HEK293T cells were transfected with Myc-Smad1 and Flag-PPM1H or its mutants as follows: Flag-N, N-terminal region of PPM1H; Flag-C, C-terminal region of PPM1H containing the catalytic domain of PPM1H; Flag-D437N. Interaction between Smad1 and PPM1H or its mutants was determined as described in A except that anti-Flag antibody was used for IP and anti-Myc antibody was used to detect PPM1H-interacting Smad1. (D) The MH2 domain of Smad1 interacts strongly with PPM1H. In vitro translated, 35S-labeled Flag-PPM1H was incubated with GST fusion protein of Smad1 or its mutants. Smad1-bound PPM1H was retrieved by glutathione beads and visualized by autoradiography. MH1, linker, and MH2 of Smad1 are shown. (E) PPM1H does not interact with Smad2. HEK293T cells were transfected with Flag-PPM1H-N together with either Myc-Smad1 or Myc-Smad2. Interaction between PPM1H-N and Smad1 or Smad2 was examined as described in C. PPM1H co-immunoprecipitated with Smad1 (lane 4) but not Smad2 (lane 5). (F) PPM1H associates with cytoplasmic Smad1. C2C12 cells were transfected with VN-PPM1H fusion and YC-Smad1 fusion, and the interaction between PPM1H and Smad1 was indicated by the fluorescence of YFP. VN-vector was used as control. DAPI: for nucleus staining.