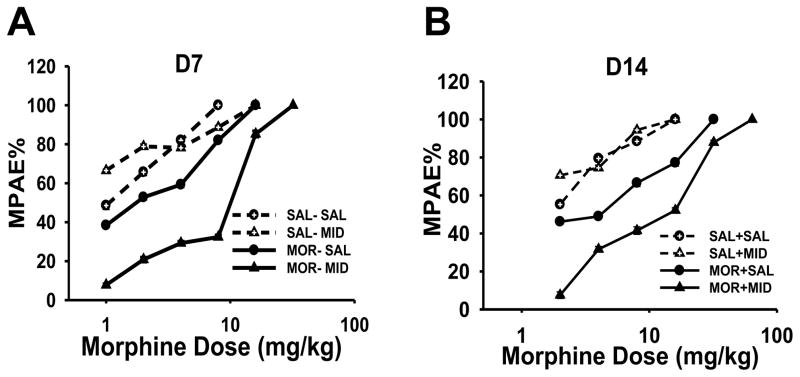
Fig. 3. Effect of midazolam on cumulative morphine dose-response curves.
Morphine anti-nociceptive dose-responses in young rats with burn injury (n=6) were assessed on day 7 (A) and day 14 (B). A rightward shift of morphine dose-response was demonstrated in burn-injured rats of MOR-SAL and MOR-MID groups on day 7 (A) and day 14 (B). And the development of morphine tolerance was exacerbated when morphine was administered with midazolam for 14 days B. ED50 and 95% confidence intervals (CI) are presented in Table 2. MPAE%: percent of maximal possible anti-nociceptive effect.
The percent of maximal possible anti-nociceptive effect (%MPAE) was determined by comparing hindpaw withdrawal latency before (baseline, BL) and after each morphine administration (TL) using the equation: MPAE% = [(TL-BL)/(20−BL) ×100% (20s as the cut-off time).