Fig. 2.
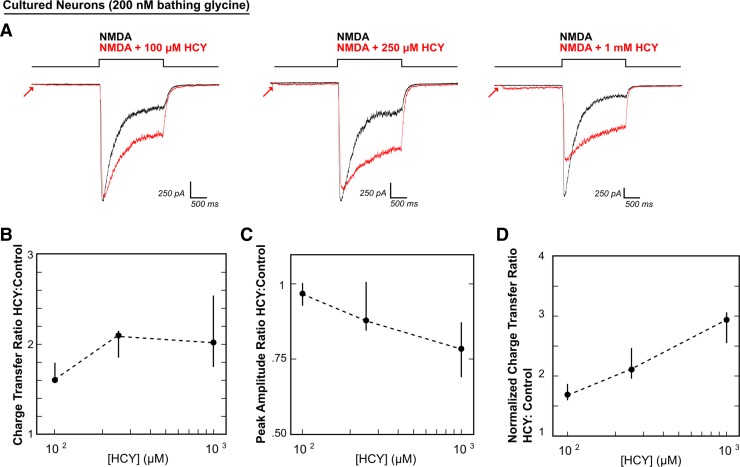
HCY effects on NMDAR current amplitude and desensitization are dose dependent. A: voltage-clamped neurons were maintained in 200 nM GLY with low extracellular calcium (0.2 mM) to prevent masking of HCY effects by calcium-dependent NMDAR desensitization. NMDA (100 μM) was applied for 2 s either with HCY or without HCY. Increasing HCY concentrations ([HCY]) decreased peak NMDAR current amplitude (A and C) and reduced desensitization (A and D) dose dependently (i.e., HCY increased normalized charge transfer: see materials and methods and Fig. 1E). Notice that HCY still strongly reduced desensitization at 1/10th of its maximal concentration (100 μM = 50 μM l-HCY isomer). There was no significant effect on amplitude at 100 μM, but a significant amplitude reduction at 1 mM HCY. This resulted in a nonmonotonic increase in charge transfer ratio (B) because, as desensitization reduction enhanced charge transfer, peak amplitude reduction decreased charge transfer (for [HCY] = 100 μM, 250 μM, 1 mM, N = 7, 5, 10).