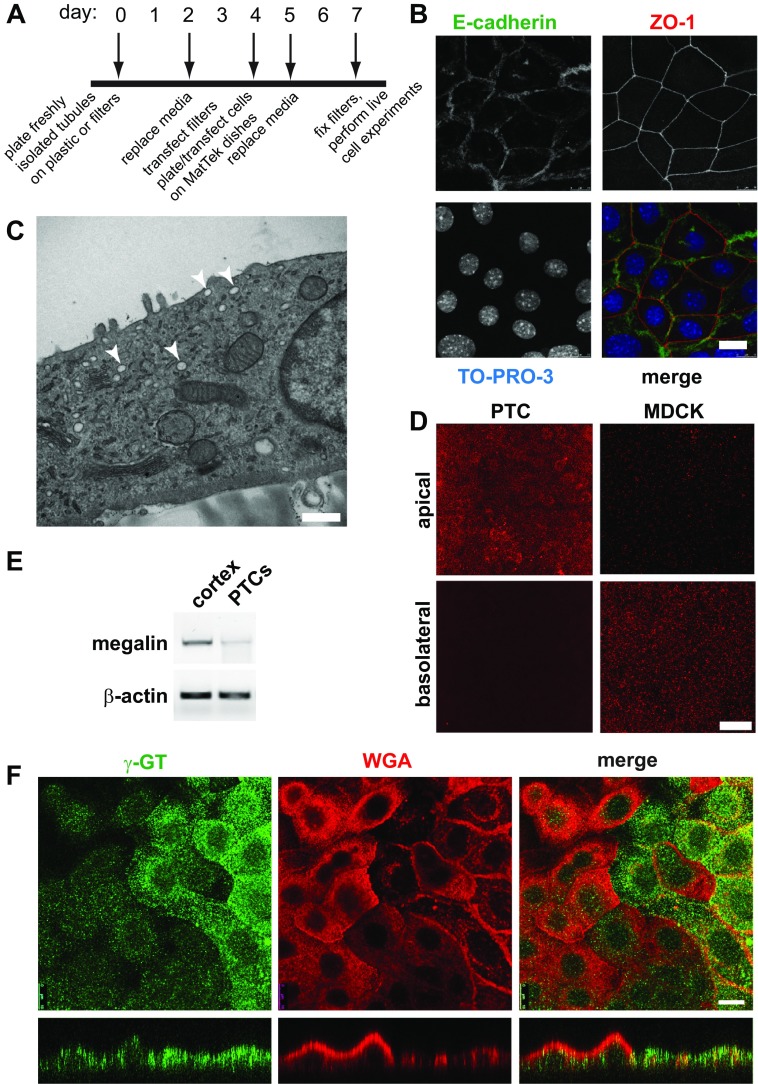
Fig. 1.
Characterization of primary proximal tubule cell (PTC) cultures. A: timeline of cell-plating schedule after isolation of PTCs from mouse kidney cortex. B: PTCs grown on permeable supports were fixed and processed for indirect immunofluorescence to detect the lateral adherens junction marker E-cadherin (green), the tight junction marker zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1; red), and nuclei using TO-PRO-3 (blue). Scale bar, 10 μm. C: PTCs grown on permeable supports were processed for transmission electron microscopy. Arrowheads denote subapical structures that may correspond to apical vacuoles observed in vivo. Scale bar, 500 nm. D: filter-grown PTCs or Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells were incubated with apically or basolaterally added rhodamine-dextran (1 mg/ml) for 20 min and processed for immunofluorescence. PTCs internalized dextran primarily from the apical surface, whereas the opposite was observed for MDCK cells. Scale bar, 15 μm. E: RT-PCR was performed to detect megalin expression from reverse-transcribed mRNA isolated from mouse cortex or from PTCs after 7 days in culture. β-Actin is included as a loading control. F: filter-grown PTCs were incubated with rhodamine-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) for 30 min (red), fixed, and then processed to detect γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (γ-GT; green). Cells were analyzed by confocal microscopy, and individual optical sections and xz reconstructions are shown. Note that cells expressing higher levels of γ-GT bind to and internalize less WGA and are markedly flatter in cross section. Scale bar, 10 μm.