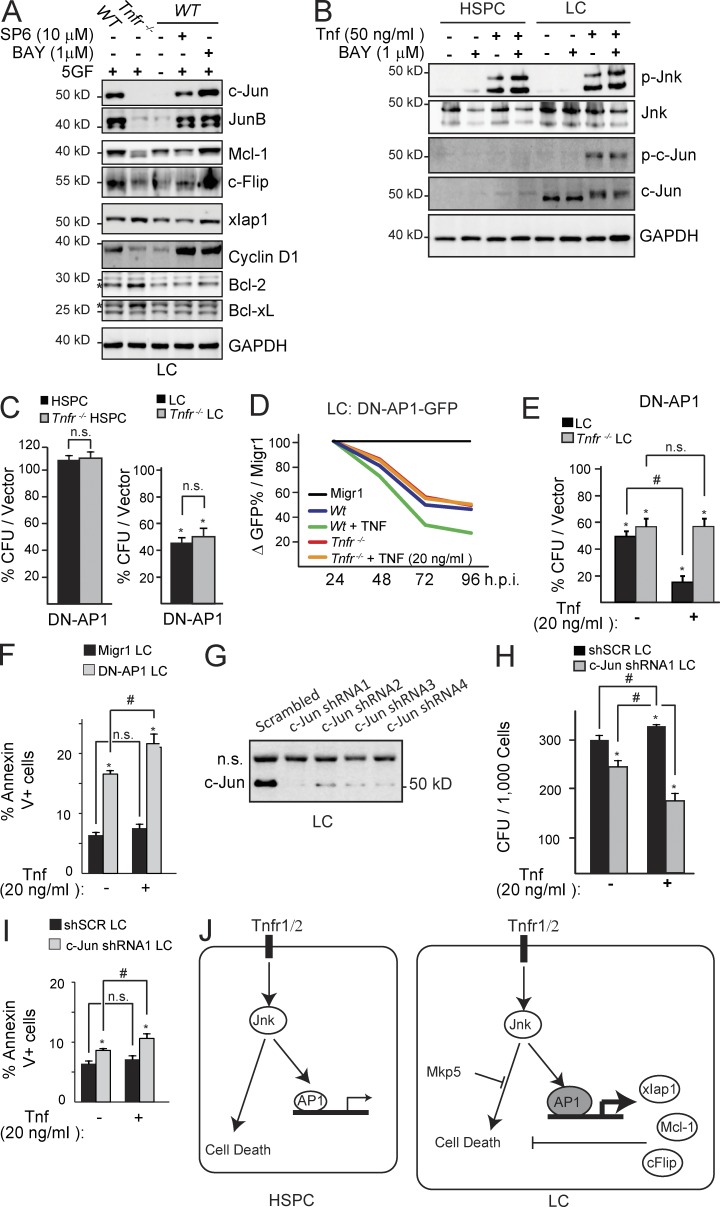
Figure 6.
c-Jun mediates the Tnf-Jnk survival signal in LC. (A) LC and Tnfr−/− LC, grown in medium containing 10% FBS, were pretreated with BAY or SP6 before addition of growth factors and Tnf. Anti-apoptotic and proliferation-related signals were examined by Western blotting. (B) HSPC and LC were pretreated with BAY followed by Tnf stimulation. p-c-Jun and c-Jun expression were examined by Western blotting. (C) HSPC and Tnfr−/− HSPC as well as LC and Tnfr−/− LC were transduced with DN-AP1 and sorted for CFU assay. (D and E) LC and Tnfr−/− LC were transduced with DN-AP1-GFP and were observed in suspension culture for reduction of GFP+ cell percentage (D) or sorted for CFU with or without 20 ng/ml Tnf treatment (E). (F) DN-AP1–transduced LCs were treated with Tnf or vehicle and assayed for cell death. (G) c-Jun knockdown by specific shRNA was verified by Western blotting. (H) c-Jun shRNA-transduced HSPC and LC were treated with TNF or vehicle and plated in methylcellulose for CFU assay. (I) c-Jun knockdown in LC enhances cell death when treated with Tnf. (J) Experiment model, a mechanism by which Jnk signal promotes survival of LC. Results shown are mean values ± 1 SD from three independent trials. * indicates P < 0.05 significant difference when compared with vehicle in E, F, H, and I, vector-only (Migr1) in C as determined by Student’s t test two-tailed analysis. # indicates P < 0.05 significant difference when compared with indicated conditions. A, B, D, and G are representative results from three independent trials.