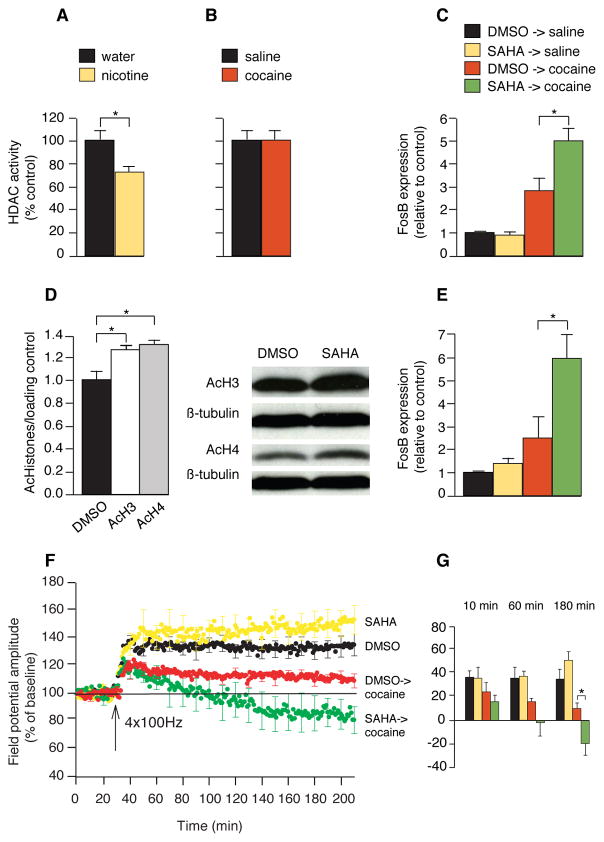
Fig. 4.
Nicotine inhibits HDAC activity and its effects are mimicked by an acetylase inhibitor. (A-B) In the nuclear fraction, an HDAC activity assay that detects deacetylation of lysine residues was performed in mice treated with nicotine (10 μg/ml) for 7 – 10 days (A) and cocaine (30 mg/kg) for 7 days (B) (n = 5–7 in each group). Data represent means ± SEM. (C) Real-time RT-PCR measuring FosB expression in animals treated with systemic SAHA (25 mg/kg i.p.) followed by cocaine compared with controls (n = 5–7 in each group). (D) Immunoblots of histone H3 and H4 acetylation after SAHA treatment (n = 3–4 in each group). (E) Real-time RT-PCR measuring FosB expression in animals treated with local SAHA (100 μM) infused to the NAc for 7 days followed by cocaine (30 mg/kg) compared with controls (n = 4–7 in each group). (F) LTP measurement in mice treated with SAHA (25 mg/kg) followed by cocaine (30 mg/kg). SAHA was given 2 hours before cocaine or saline injections (n = 5 to 6). Field potential amplitudes were measured in the core of the NAc. (G) Histogram summary of time course of SAHA and cocaine effects on LTP. *P < 0.05.