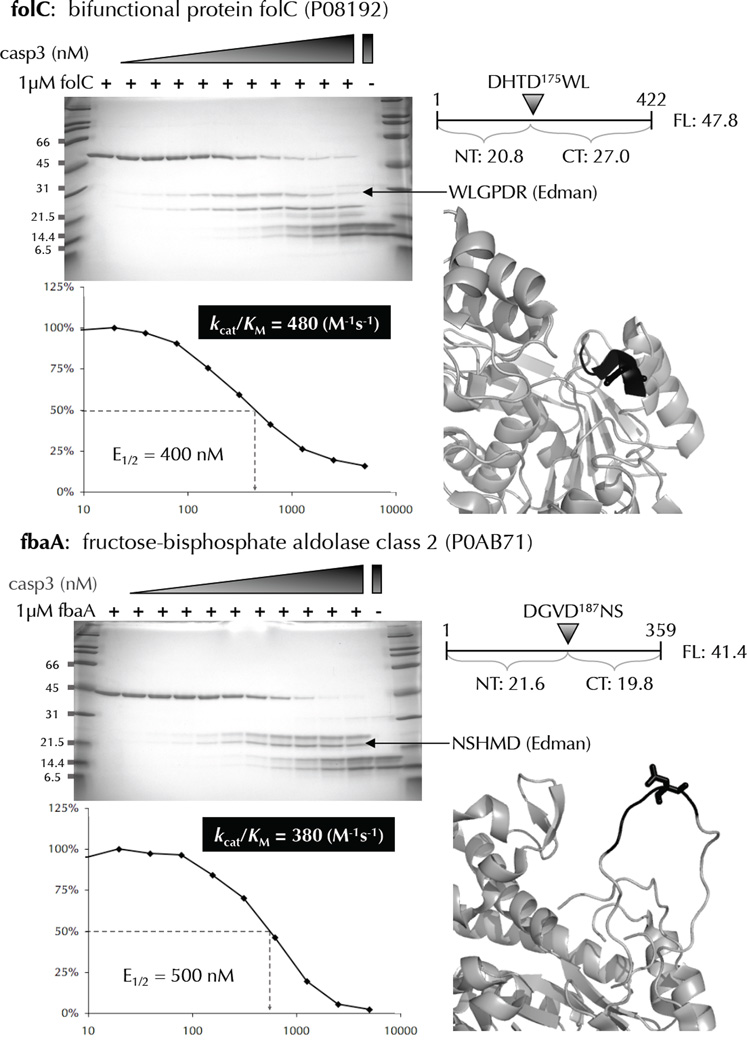
Figure 6.
Biochemical and kinetic analysis of cleavage-sites identified by N-terminomics. Many E. coli proteins that were identified as substrates of human caspase-3, and containing only 1 cleavage-site were recombinantly expressed, purified, and subjected to in vitro cleavage by human caspase-3. The cleavage-site P4-P1’ amino acids are colored black with the P1 residue in stick format. Substrate cleavage-sites were identified by N-terminal sequencing of the proteolytic fragments using Edman degradation. The E1/2 values were measured based on the disappearance of the full-length substrate using densitometry. These values were used to calculate kcat/KM for each substrate.