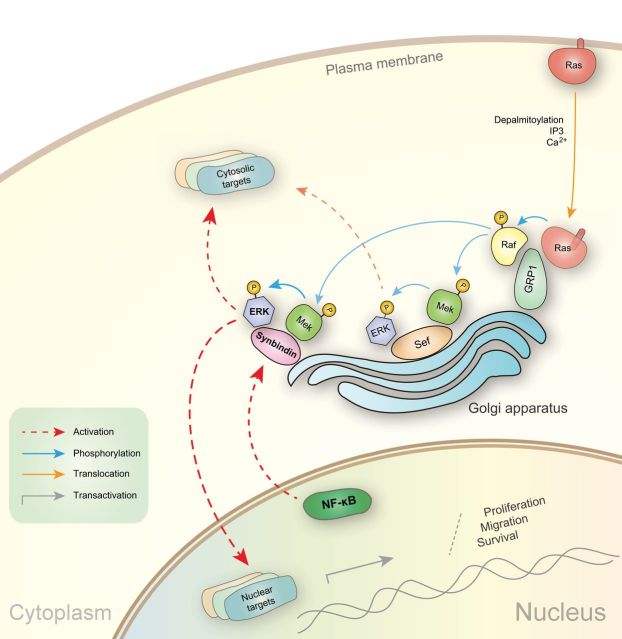
Figure 7.
Schematic representation showing the proposed mechanism. The Golgi apparatus has been found as an important compartment for the Ras-Raf-Mek-ERK pathway. The association of Ras to Golgi has been shown to involve depalmitoylation, IP3, and calcium. The GRP1 protein anchors both Ras and Raf on the Golgi apparatus, which leads to the activation of Raf kinase. The Sef protein is another MAPK scaffold molecule on the Golgi, which binds to active MEK/ERK complexes and allows signaling to cytosolic targets such as RSK but not nuclear substrates such as Elk-1. We found that synbindin binds to ERK2 on the Golgi and promotes the phosphorylation of ERK2. This leads to the activation of ERK targets in both cell nucleus and cytosol. Synbindin also regulates cell cycle/apoptosis-related genes and affects cell proliferation, survival, and migration. The inflammatory inducer NF-κB directly transactivates synbindin, which explains the effect of NF-κB on cell transformation under inflammatory conditions.