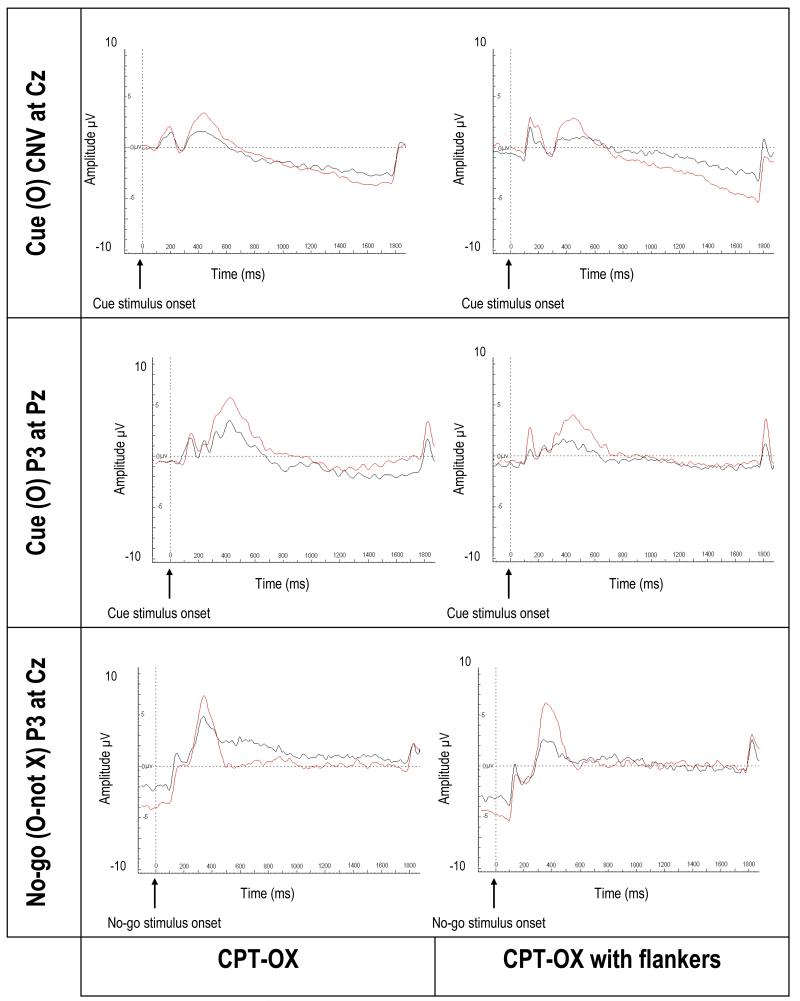
FIGURE 3. Event-related potentials associated with cue and no-go stimuli in a CPT-OX task in ADHD adults and controls (Ref. 152).
In the cued continuous performance test (CPT-OX), participants are instructed to respond to cue-target sequences (i.e. O followed by X). In the Flanker version, letters are flanked by distractor letters on either side. The figure shows CNV and stimulus-locked centro-parietal cue-P3 (in response to the cue stimulus) and no-go-P3 (enhanced positivity at fronto-central locations in response to no-go stimuli) averages for controls (red) and ADHD (black). In ADHD, a reduced CNV indicated abnormal anticipation and preparation, and reduced cue-P3 amplitudes indicated reduced attentional orienting, to cue stimuli. Attenuation of the no-go-P3 indicated the presence of abnormal inhibitory processing in adult ADHD. Figure reproduced from Ref. 144. Abbreviations: ADHD, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; CNV, contingent negative variation.