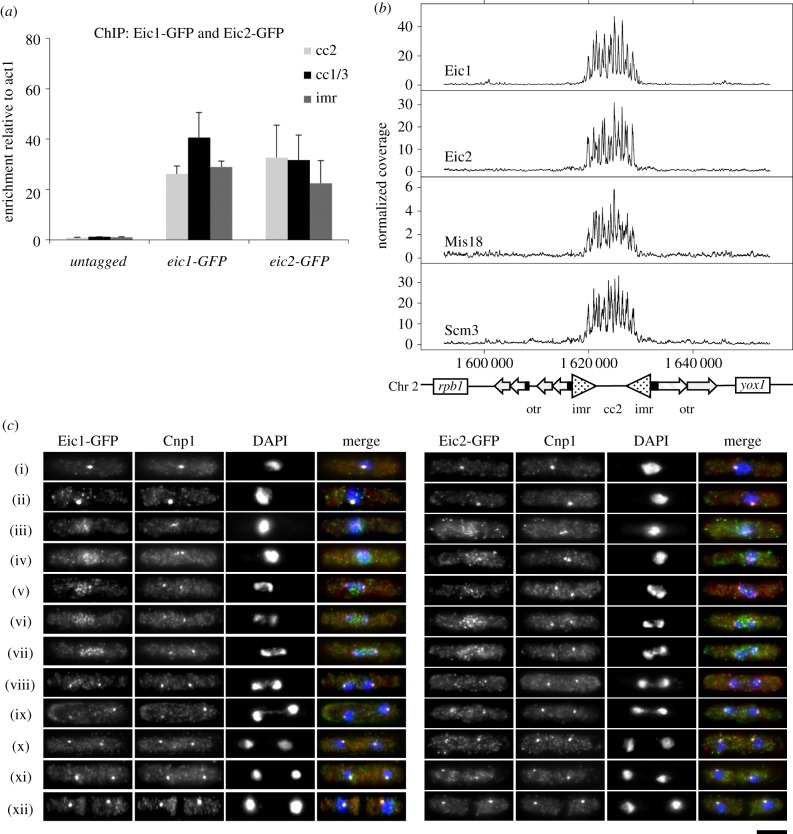
Figure 2.
Eic1 and Eic2 associate specifically with centromeres. (a) Eic1 and Eic2 bind the central domain of S. pombe centromeres. qChIP analyses showing enrichments of GFP-tagged Eic1 and Eic2 at the central cores (cc) of centromeres 1, 2 and 3 and imr repeats of centromere 1, relative to the act1 locus. Error bars represent standard deviation between at least three biological replicates. (b) Eic1 and Eic2 exhibit very similar genome-wide association profiles as Mis18 and Scm3HJURP. A comparison between the ChIP-seq profiles of GFP-tagged Eic1, Eic2, Mis18 and Scm3 across centromere 2 is presented, alongside a schematic diagram of centromere 2 (bottom). Normalized coverage represents the number of sequencing fragments obtained from anti-GFP IP normalized to that obtained from the input. (c) Eic1 and Eic2 exhibit very similar cell-cycle localization dynamics as Mis18 and Scm3HJURP. Immunofluorescence of S. pombe cells expressing GFP-tagged Eic1 or Eic2 stained with antibodies to GFP (green) and Cnp1CENP-A (red), and DAPI (blue). Both Eic1 and Eic2 dissociate from centromeres during prometaphase to mid-anaphase of mitosis ((iii)–(vii)) and subsequently reassociate. Scale bar, 5 μm.