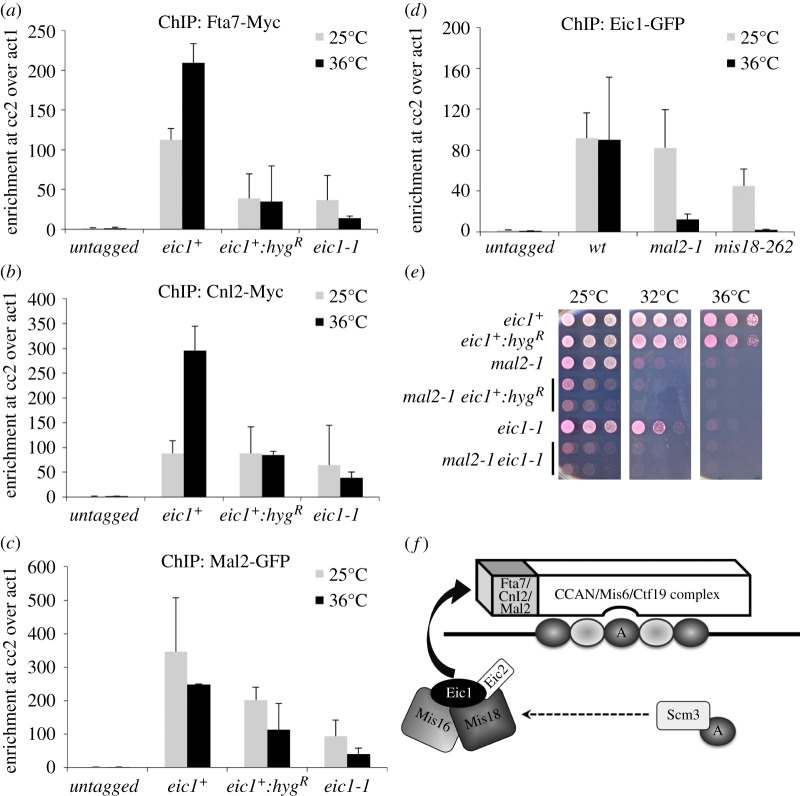
Figure 8.
The CCAN components Fta7CENP-Q/Okp1, Cnl2Nkp2 and Mal2CENP-O/Mcm21 influence Eic1 association with centromeres. (a) Fta7-Myc, (b) Cnl2-Myc and (c) Mal2-GFP association with centromeres is partly dependent on Eic1. (d) Eic1-GFP association with centromeres is greatly dependent on Mal2. qChIP analyses of (a) Fta7-Myc, (b) Cnl2-Myc, (c) Mal2-GFP and (d) Eic1-GFP association with centromeres in the indicated strains when grown at permissive (25°C) versus restrictive temperature (36°C) for 8 h. Enrichment of cc2 DNA relative to the act1 locus is presented. Error bars represent standard deviation between at least three biological replicates. (e) eic1-1 displays a severe negative genetic interaction when combined with mal2-1. Five-fold serial dilutions of cells spotted on YES + Phloxine B media and incubated at the indicated temperatures; dead cells stain dark pink. (f) A model for Cnp1CENP-A maintenance at S. pombe centromeres mediated by Eic1. The CCAN components Fta7CENP-Q/Okp1, Cnl2Nkp2 and Mal2CENP-O/Mcm21 that are constitutively bound to centromeres together form a module that recruits Eic1, and thereby regulates the temporal association of Eic1, Mis16RbAp46/48/Hat2, Mis18 and Eic2 with centromeres. Once bound, Mis16RbAp46/48/Hat2/Mis18 then likely recruit the Cnp1CENP-A-specific chaperone Scm3HJURP to centromeres (the dashed arrow indicates that only an in vitro association between these proteins has been demonstrated), and thus ensures replenishment of Cnp1CENP-A (‘A’ in closed oval) at centromeres in every cell cycle.