Table 2.
Nomenclature and base parameter values used in simulations.
| symbol | description | value | units | source/notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | water vapour concentration | mol m–3 | ||
| s | liquid water saturation | — | ||
| T | plant temperature | °C | ||
| p | water pressure | Pa | ||
| pa | vapour pressure | Pa | ||
| ul | Darcy velocity | m s–1 | ||
| Ψ | total water potential | Pa | ||
| η | leaf half-width function | m | ||
| E | transpiration rate (mass flux) | kg m–2 s–1 | ||
| W | water loss | kg | ||
| psat(T) | saturation pressure function | 0.068105T3 + 0.1145T2 + 56.920T + 594.95 | Pa | cubic fit to saturation pressure data for 0 to 45°C [8] |
| t | time | s | ||
| th | time | h | ||
| g | acceleration due to gravity | 9.8 | m s–2 | |
| ϕ | porosity of leaf/stem | 0.5 | — | |
| ρl | density of liquid water | 1000 | kg m–3 | |
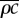
|
density–heat capacity product for leaf/petiole | 2 × 105 | J K–1 m–3 | |
| T∞ | ambient air temperature | 20–40 | °C | for comparison with Crawford et al. [2] |
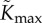 |
maximum xylem hydraulic conductance | 10−7 | s | manually fitted to give temperature variations and water loss of order of magnitude reported in Crawford et al. [2]. Note, [23] has 5 × 10−8 for different plant |
| α | fitting parameter for vulnerability curve | 1 | Pa–1 | |
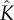
|
thermal conductivity of partially saturated leaf | 0.1 | W m–1 K–1 | all leaves in Hays [45] of order of 0.1 |
| D | diffusion coefficient of water vapour in air | 2.5 × 10−5 | m2 s–1 | average value taken from Beguerisse et al. [33] for T = 20−30°C |
| gw | transpiration capacitance-conductivity function | 3 × 10−5 | m–1 s | manually fitted to give temperature variations and water loss of order of magnitude reported in Crawford et al. [2] |
| cl | specific heat of liquid water | 103 | J kg–1 K–1 | |
| p0 | reference pressure for water retention fitting | Pa | for leaf water potentials of order of 1 MPa [8,46] | |
| np | index parameter for water retention fitting | 1 | — | |
| hplant/air | heat transfer coefficient (plant–air) | 10 | W m–2 K–1 | average for leaves studied in Linacre [47] |
| M | molar mass of water | 1.8 × 10–2 | kg mol–1 | [33] |
| R | universal gas constant | 8.31 | J mol–1 K–1 | [33] |
| λ | open stomata area fraction | 0.024 | — | estimated from data in Crawford et al. [2] |
| Lleaf | leaf axial length | 0.03 | m | of order of largest leaves in Crawford et al. [2] |
| ηmax | half maximum leaf width | 0.01 | m | of order of largest leaves in Crawford et al. [2] |
| r | petiole radius and leaf thickness | 0.0004 | m | of order of leaf thickness in Crawford et al. [2] |
| qsoil | soil surface–air mass transfer coefficient | 0 | m s–1 | |
| C∞ | vapour concentration at boundary | 0.5 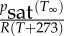
|
mol m−3 | growth cabinet humidity of the order of 50% |
| m1,2 | ratio of petiole to leaf length | — | ||
| β1,2 | petiole angle to soil surface | ° |
