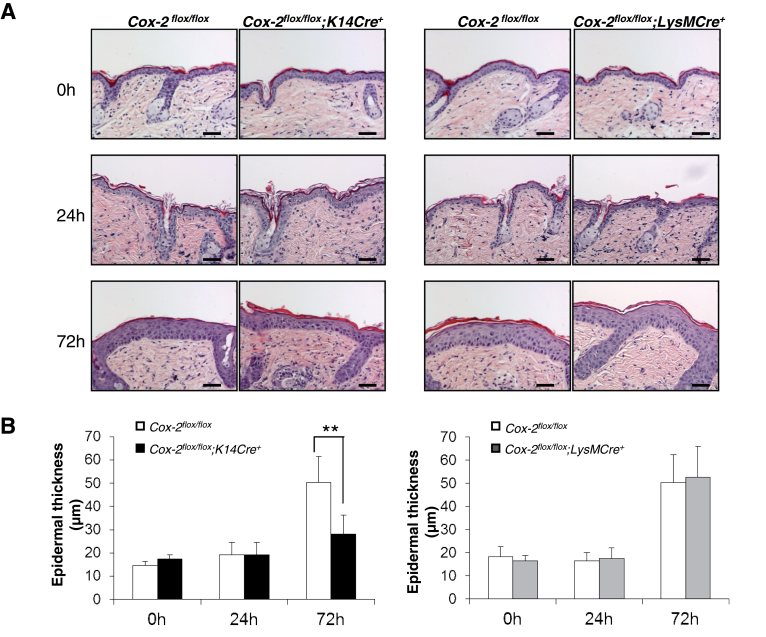
Fig. 3.
Epidermal hyperplasia is reduced in response to UVB irradiation in mice with an epidermal cell-specific Cox-2 gene deletion but is not affected in UVB-irradiated mice with a myeloid cell-specific Cox-2 gene deletion. (A) H&E sections from the skin of Cox-2 flox/flox ;K14Cre + mice (n = 4) and their littermate Cox-2 flox/flox mice (n = 4), and from skin of Cox-2 flox/flox ;LysMCre + mice (n = 4) and their littermate Cox-2 flox/flox mice (n = 4) at the times shown following a single UVB irradiation. After UV irradiation, Cox-2 flox/flox ;K14Cre + mice exhibit decreased epidermal hyperplasia compared with littermate Cox-2 flox/flox mice. (B) Quantification of epidermal thickness. Error bars are standard deviation. **P < 0.01. Scale bar: 50 µm.