Figure 4.
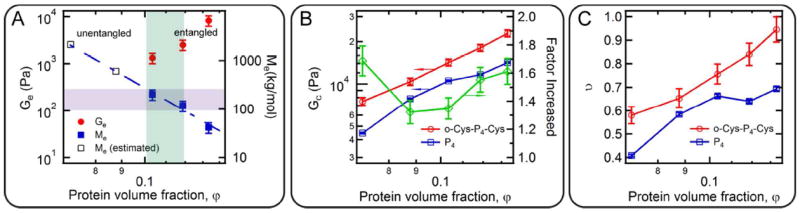
The contribution of chain entanglement and coiled-coil association to network mechanics. (A) Entanglement plateau modulus and the entanglement molecular weight as a function of protein concentration. The purple shaded area highlights the estimated molecular weight (from the lowest Mn to the highest Mw) from the analysis based on the Jacobson-Stockmayer theory. The green shaded area marks the experimentally observed onset of chain entanglement. (B) Comparison of plateau modulus contributed by coiled-coil association as a function of protein concentration at 25 °C (red for hydrogel o-Cys-P4-Cys, and blue for hydrogel P4). Data in green showing the ratio of the two moduli at the same concentration. (C) Comparison of the fractions of elastically effective chains in o-Cys-P4-Cys and P4. Error bars represent the standard deviations of the measurement. (N = 3)
