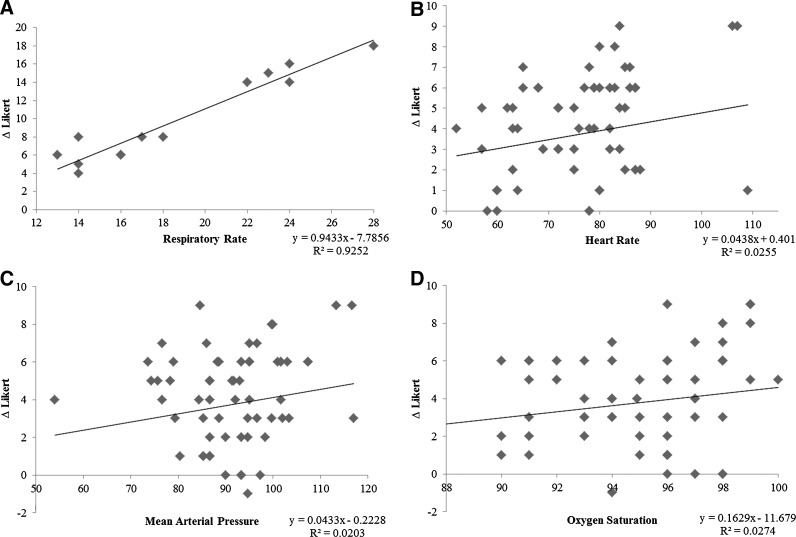
FIG. 1.
Correlation of physiological factors with change in subjective pain measurements. (A) Patients' initial respiratory rates and change in subjective responses were measured against each other. Upwards trend line indicates that patients with higher respiratory rates experienced a larger decrease in their reported pain. (B) Subjects with higher initial heart rates generally reported a larger decrease in pain post-therapy, while other subjects with lower to normal heart rates indicated little to no change in pain. (C) Initial mean arterial pressure and change in subjective ratings showed slight positive correlation. (D) Initial oxygen saturation and change in subjective pain responses showed slight correlation, possibly explained by the small range of possible oxygen saturation within healthy subjects.