Fig. 5. Abnormal expression of Shh and Shh target genes, Gli1 and cyclin D1, in conditional Kif3a mutants.
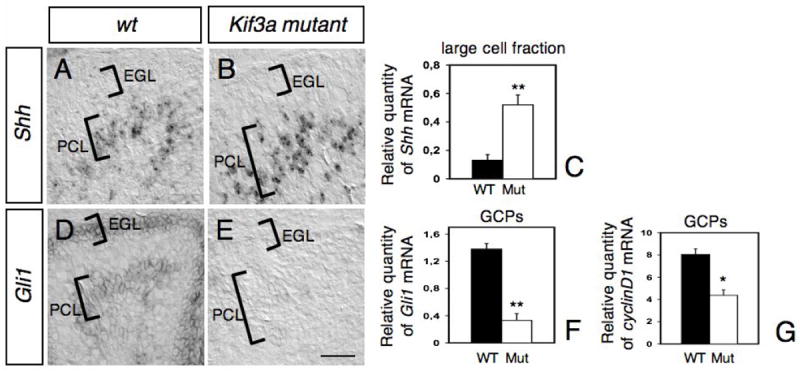
In situ hybridization on sagittal sections of wild type (A, D) and mutant (B, E) cerebellum at P2 with antisense riboprobes specific for Shh (A-B) and Gli1 (D-E). The location of the EGL and PCL are indicated on each panel. Note that whereas Shh expression is increased in the PCL of mutant compared to wild-type (A-C), Gli1 was no longer detected neither in the EGL nor the PCL in the mutant (E). (C, F-G) Levels of Shh mRNAs in the large cell fraction enriched in Purkinje cells (C), and levels of Gli1 (F) and cyclin D1 mRNAs in GCPs (G) at P2-4 were evaluated by semi-quantitative real-time RT-PCR and are shown as the relative quantities normalized to the level of hprt mRNA expression. The level of Shh mRNA in conditional Kif3a mutant is significantly higher than that in the wild-type, whereas the levels of Gli1 and cyclin D1 mRNAs in the mutant are significantly lower than those in the wild-type. Each column and the vertical line represent the mean± SEM. Data from three mice per group were pooled for statistical analysis with Student’s t-test. *: p<0.05; **: p<0.01. Scale bar: 80 μm.
