Figure 2. Cre mRNA is present in the blood plasma of Vav-iCre mice and contained in EVs including exosomes.
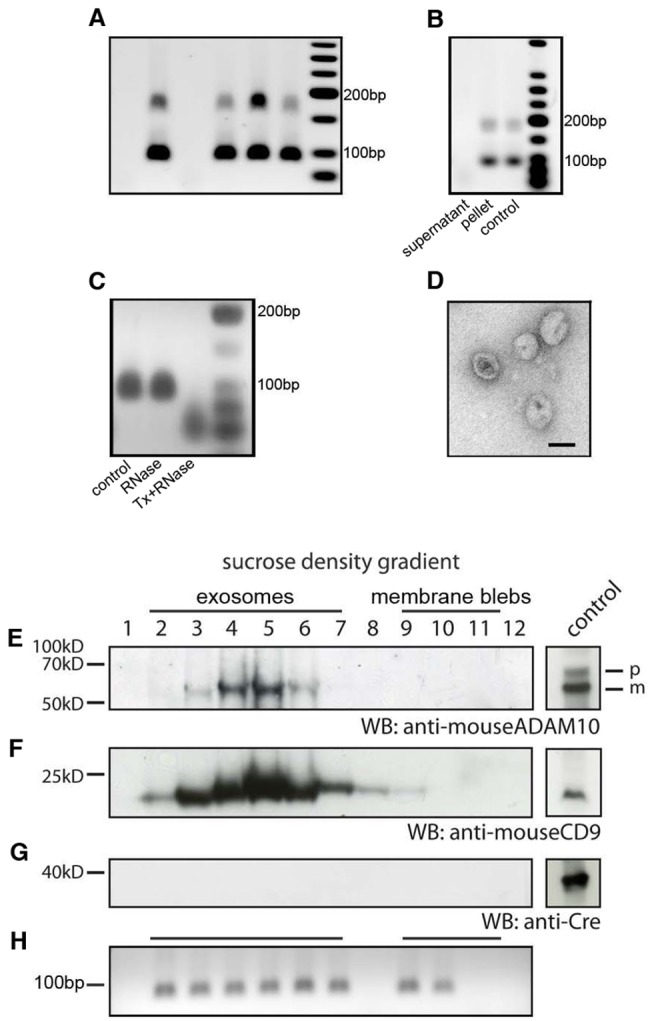
(A) Cre mRNA can be detected in vesicle preparations enriched for exosomes from the blood plasma of Vav-iCre mice by RT-PCR. Each lane represents a result from an individual animal. For detection of Cre mRNA, nested primer PCR was used. The PCR product at 100 bp represents the signal after the second round of amplification. (B) Cre mRNA is localized in the pellet but not in the supernatant after ultracentrifugation of conditioned medium from primary Vav-iCre–positive hematopoietic cells after stimulation by LPS in vitro. Cre mRNA was resistant to RNaseA treatment in all experiments. (C) After treatment with Triton-X to lyse EVs in combination with RNaseA digestion, Cre mRNA is no longer detectable in contrast to RNaseA treatment alone. (D) Vesicular structures between 50 and 100 nm in size were visualized in electron micrographs from Vav-iCre hematopoietic-cell-derived vesicle preparations (scale bar, 50 nm). (E and F) Secreted membrane vesicle subspecies can be separated by density by sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation. Exosomal identity was confirmed by blotting against the specific protein markers ADAM10 and CD9 for all subfractions. (G) Cre protein could not be detected in any of the fractions. Positive controls for all antibodies are shown in boxes to the right. (H) Cre mRNA is present in the exosomal fractions 2–7. The nonexosomal vesicles fractions or apoptotic bodies are characterized by their variability of positive subfractions to complete absence of Cre mRNA. In this experiment, subfractions 9 and 10 are positive, whereas 8, 11, and 12 do not contain any Cre RNA.
