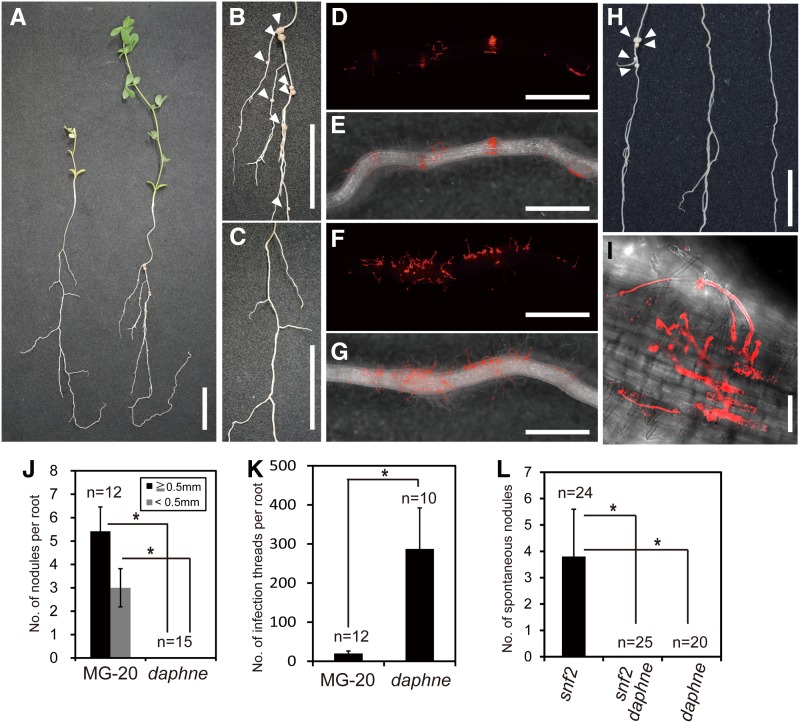
Figure 1.
Isolation of a novel nonnodulation mutant, daphne. A, Shoot and root phenotypes of the daphne mutant (left) and the Miyakojima MG-20 wild type (right) at 28 DAI. B, Nodulation phenotype of Miyakojima MG-20. Arrowheads indicate nodules. C, The nonnodulation phenotype of daphne. D to G, IT formation of the Miyakojima MG-20 root (D and E) and of the daphne root (F and G) following inoculation with M. loti MAFF303099 constitutively expressing DsRED. D and F, Red fluorescence images of roots. Linear red signals indicate ITs. E and G, Red fluorescence images and transmitted light images are merged. H, Spontaneous nodule formation in snf2 (left), the daphne snf2 double mutant (middle), and daphne (right). Arrowheads indicate spontaneous nodules. I, Confocal microscopic image of a daphne root. Z-stack series are shown in Supplemental Figure S2. Bars = 2 cm in A to C and H and 1 mm in D to G. J, Nodules were counted at 28 DAI with M. loti MAFF303099. K, The number of ITs per root was counted at 7 DAI with M. loti MAFF303099 constitutively expressing LacZ. L, Six weeks after germination, spontaneous nodules were counted without rhizobial infection under the no-nitrogen condition. Error bars indicate sd. *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test.