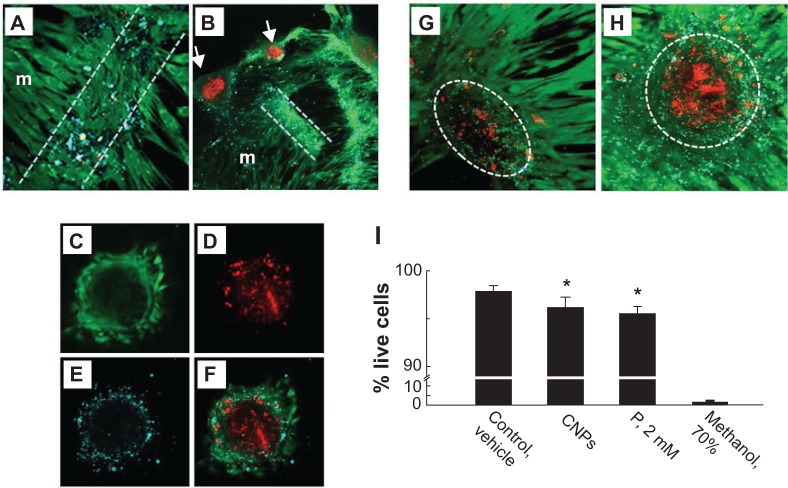
Figure 5.
Confocal micrographs identifying apoptosis and necrosis in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells treated with CNPs.
Notes: Prior to confocal imaging, CNP-treated (A–F,H) and vehicle-treated control (G) cells were incubated with calcein-AM, EthD-1, and annexin V-AlexaFluor® 647 conjugate (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to label live cells (green), dead (red) cells, and apoptotic bodies (cyan), respectively. After several days in culture, monolayer cells (m) contracted into ridges (between white lines) with associated apoptotic bodies (A). Ridges later developed into nodules (arrows) comprising a core of dead cells, with live cells and apoptotic bodies peripherally (B). Maximum-intensity projection of 14 optical sections through the mid-portion of a nodule shows live (C), dead (D), and apoptotic (E) cells; (F) shows a composite image. Representative maximum-intensity projections of 76 optical sections through whole individual nodules of vehicle-treated cells (G) typically displayed less labeling for fragmented nuclei and apoptotic bodies than did a comparable projection of CNP-treated cells (H). Dotted outlines (G,H) encompass one nodule. Monolayer cell viability at day 28, determined by live/dead cell counting, was significantly reduced by CNPs and by 2 mM P; cells preexposed to 70% methanol served as dead cell control (I). *Significant difference (P<0.05) from control; n=9–10 each.
Abbreviations: CNP, calcifying nanoparticle; EthD-1, ethidium homodimer-1; P, phosphate; AM, acetoxymethyl ester.