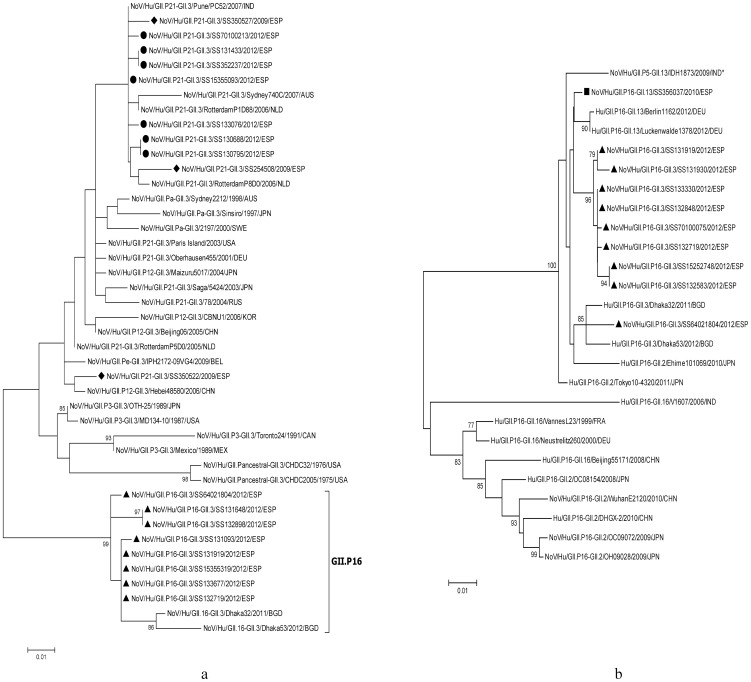
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analyses of GII.3 and GII.P16 norovirus recombinant strains.
a) partial capsid (ORF2) GII.3 gene (259 nt) and b) partial polymerase (ORF1) GII.P16 gene (719 nt), from distinct patients with acute gastroenteritis, detected in Gipuzkoa (Basque Country, Spain) in 2009–2012, compared with some representative strains. The trees were constructed in Mega 6 through the Maximun Likelihood method using the best model, Kimura 2-parameter+G, as determined also in Mega 6 using the Bayesian information criterion, with 1000 bootstrap replications for branch support. Bootstrap values >75% are shown. Scale bars indicate the number of substitutions per nucleotide position. Norovirus strains detected in this study are marked with the following symbols: ▴, GII.P16-GII.3; ▪, GII.P16-GII.13; ♦, GII.P21-GII.3 detected in 2009; •, GII.P21-GII.3 detected in 2012. a.- Capsid (ORF2). b.- Polymerase (ORF1). Footnote (figure 1b). *When this sequence was analyzed in the Noronet typing tool, was classified as GII.P16/GII.13.