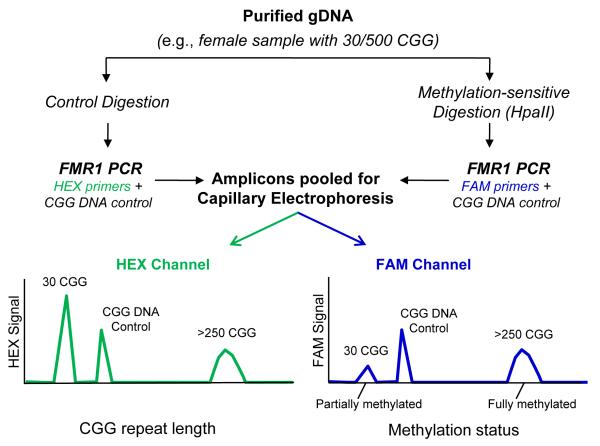
Fig. 1. mPCR-CE procedural work flow for the determination of methylation status of FMR1 alleles.
Methylation status was assessed by comparing an aliquot of genomic DNA treated with HpaII and amplified with a FAM-labeled primer to an undigested aliquot amplified with a HEX-labeled primer. Unmethylated alleles were digested and thus unamplifiable in the subsequent PCR step, whereas methylated alleles were undigested and amplifiable by PCR. A plasmid CGG-rich DNA control was included in each PCR to normalize well-towell differences in PCR amplification and CE detection efficiency. Following PCR, amplicons from both reactions were pooled and injected in a single capillary. In the resulting electropherogram, the CGG repeat length was determined in the HEX channel and the percent methylation computed using a normalized ratio of signals in the FAM channel.