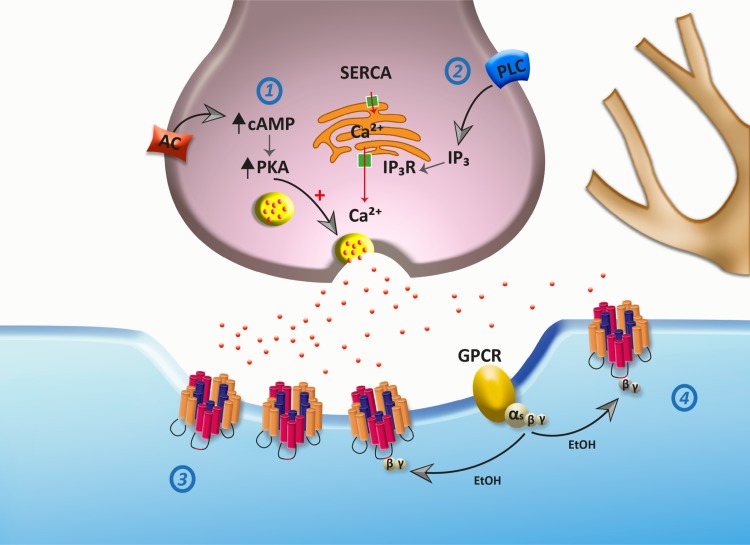
Fig. 7.
Scheme of proposed ethanol effects on glycinergic synapses. At the presynaptic level, ethanol increases vesicular glycine release (red dots) by activation of adenylate cyclase (AC)/PKA (1) and PLC/inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) receptor (IP3R)/Ca2+ (2) pathways. Here, AC activation can increase PKA activity, leading to vesicular release. The data also support the idea that ethanol increases intracellular calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by IP3R activation. At the postsynaptic level, GlyRs are located at synaptic (3) and nonsynaptic (4) sites. Modulation of GlyRs by Gβγ protein plays a key role in ethanol effects.