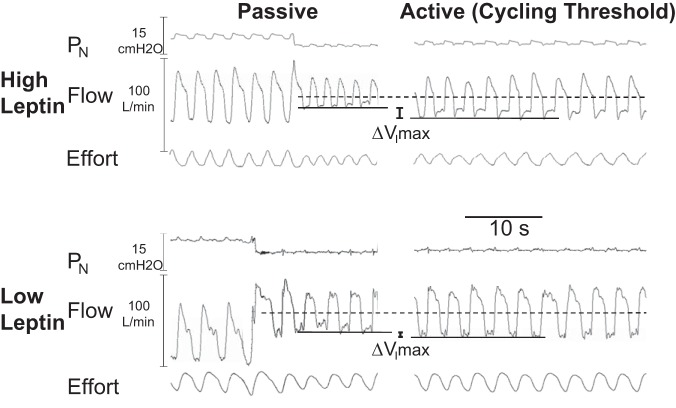
Fig. 1.
Compensatory differences in peak inspiratory airflow (ΔVImax) responses in a subject with a high circulating leptin (top) compared with one with a low circulating leptin (bottom) concentration (156 vs. 35 ng/ml, respectively). In each subject, an abrupt drop in nasal pressure was associated with the onset of inspiratory flow limitation acutely (left) in the passive state. Maintaining nasal pressure near the cycling threshold (right), however, resulted in an increase in VImax (top right) or little change in VImax (bottom right), indicating a greater compensatory response in the subject with high compared with low leptin concentration.