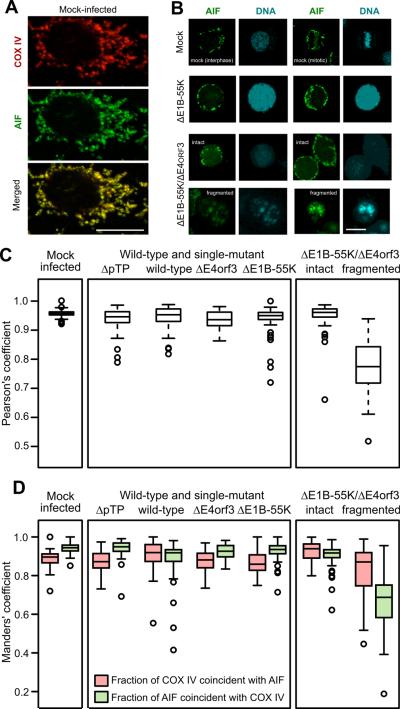
Figure 4.
AIF is found outside the mitochondria in cells with fragmented nuclei. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated viruses at an MOI of 10, processed for immunofluorescence at 72 hpi, and imaged by confocal microscopy. Representative images are shown in panels A and B. The scale bar indicates 10 μm. The virus identified as ΔpTP bears a deletion in the preterminal protein gene and is unable to direct viral DNA replication. (A) Staining for AIF and the mitochondrial marker COX IV is coincident in the mock-infected cells. (B) AIF remains in the cytoplasm in mock-infected cells and cells infected with the E1B-55K-mutant virus. Nuclear translocation of AIF is seen only in cells with fragmented nuclei following infection with the E1B-55K/E4orf3 double-mutant virus. (C) The coincidence of AIF and COX IV was determined in at least 50 cells and quantified with the Pearson's correlation coefficient. Cells infected with the double-mutant virus were stratified into those with intact nuclei and those with fragmented nuclei. (D) Manders' coefficients of overlap were determined to quantify the proportion of COX IV staining that is coincident with AIF staining (red symbols) and the proportion of AIF staining that is coincident with COX IV staining (green symbols).