Figure 4.
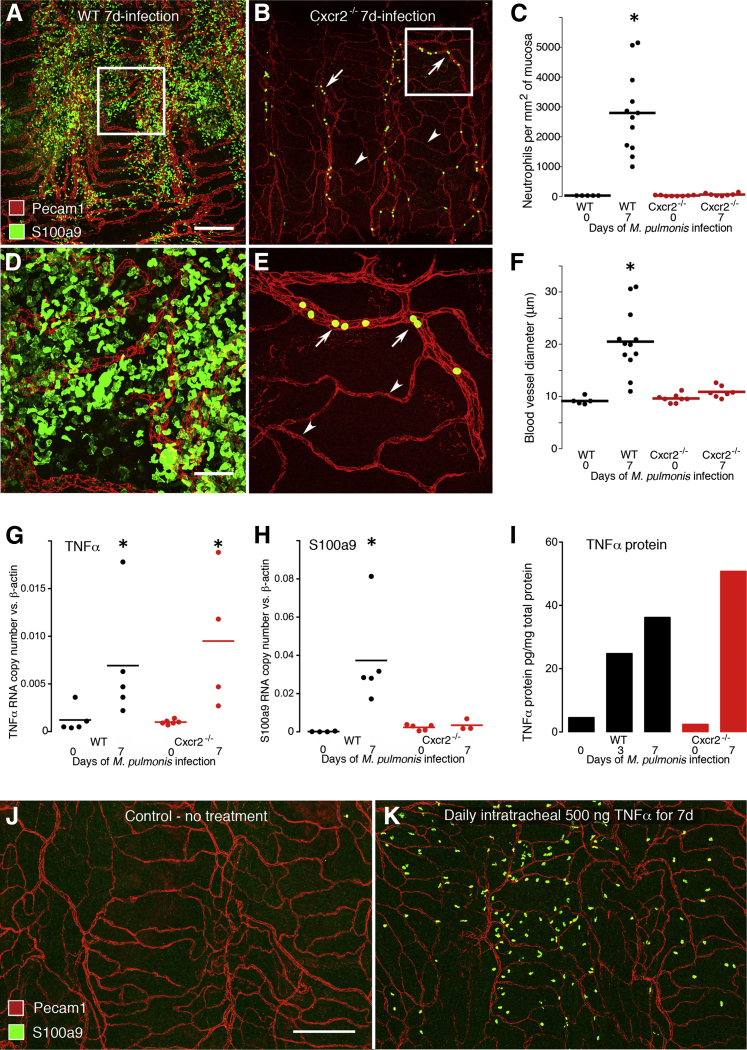
Changes in TNFα and dependence of neutrophil influx and vascular remodeling on Cxcr2 signaling. Whole mounts of mouse trachea comparing the number and distribution of neutrophils (S100a9, green) in relation to blood vessels (Pecam1, red) in wild-type (WT) and Cxcr2−/− mice at day 7 of infection (A, B, D, and E). A and B: Low-magnification view comparing widespread neutrophils in a WT mouse and sparse neutrophils in a Cxcr2−/− mouse. Most of the latter are inside venules (arrows) but not in capillaries (arrowheads). C: Measurements per mouse and group means show extensive neutrophil influx after infection of WT mice but not of Cxcr2−/− mice. N = 5 to 12 mice per group; ∗P < 0.05 compared with the pathogen-free group. D and E: Higher magnification view of boxed areas in A and B show abundant neutrophils after infection in a WT mouse and sparse neutrophils in a Cxcr2−/− mouse. F: Blood vessel diameters show prominent enlargement at day 7 of infection in WT mice but not in Cxcr2−/− mice. N = 5 to 12 mice per group; ∗P < 0.05 compared with the pathogen-free group. G and H: TNFα (G) and S100a9 (H) mRNA expression assayed by RT-qPCR in pathogen-free and 7-day M. pulmonis–infected WT mice (black circles) and Cxcr2−/− mice (red circles). After infection of WT mice, the expression of both TNFα and S100a9 were significantly greater than in pathogen-free controls, but in infected Cxcr2−/− mice, TNFα was greater but S100a9 was not different from the corresponding pathogen-free value. N = 4 to 6 mice per group, ∗P < 0.05. I: TNFα protein levels in tracheas of pathogen-free mice and M. pulmonis–infected WT mice assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Tracheas were pooled (from N = 5 to 6 mice/group) to yield enough protein for analysis. J and K: Confocal images of whole mounts of tracheas, stained for blood vessels (Pecam1, red) and neutrophils (S100a9, green), from pathogen-free mice that were untreated (J) or given 500 ng of recombinant mouse TNFα (K) daily for 7 days by intratracheal instillation. No evidence for vascular remodeling was evident in the TNFα-challenged trachea, although neutrophils were more numerous than in untreated controls. Scale bars: 200 μm (A, B, J, and K); 50 μm (D and E).