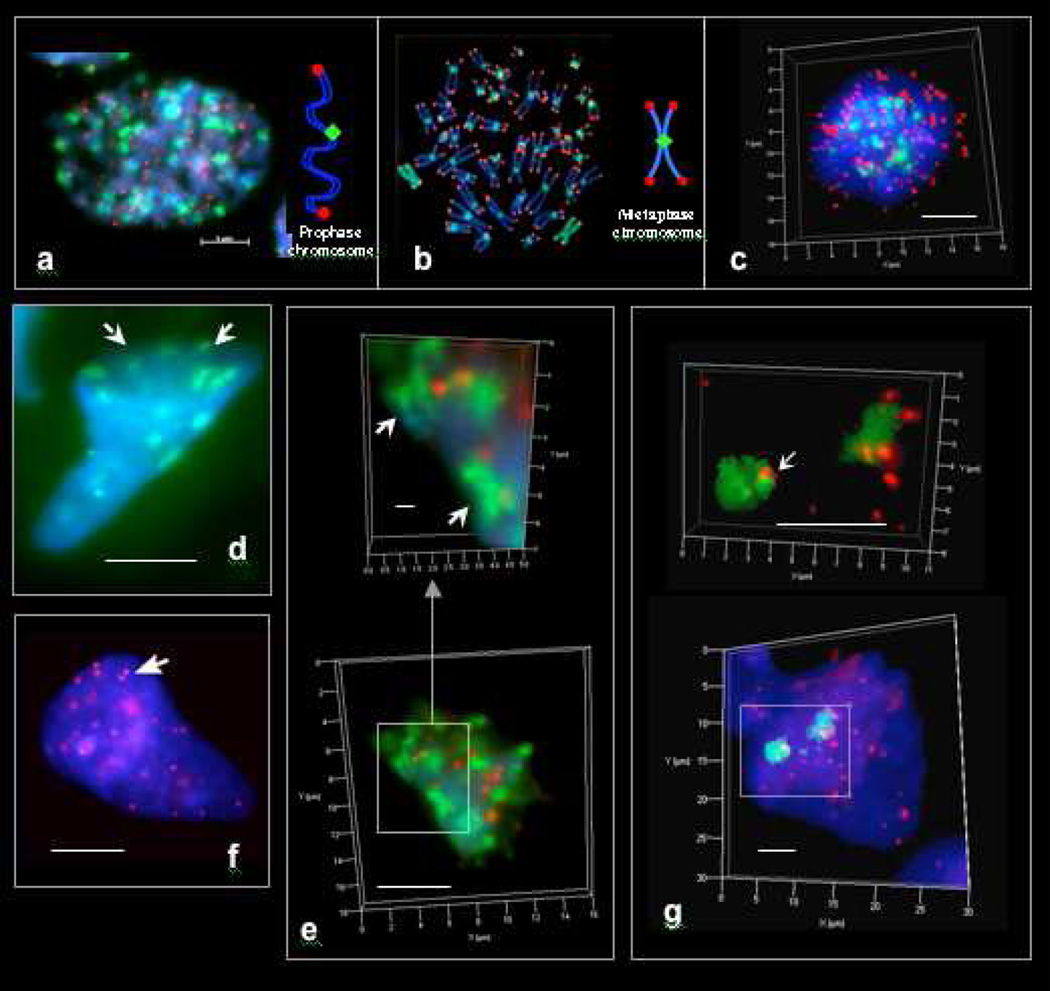
Figure 1. Pan-centromeric (FITC, green) and pan-telomeric (Cy3, red) FISH staining regions in cells and syncytia of early human fetuses and tumors.
a. Fetal mitotic (eukaryotic) nucleus (colon, 12 wks) in early prophase. b. Cultured human mitotic (eukaryotic) lymphoblastoid cell nucleus (TK6) in metaphase. c. Metaphase of fetal colonic mitotic cell as seen in 3D imaging. 46 centromeric and 92 telomeric staining regions appear in eukaryotic prophases. 46 centromeric and ~ 184 telomeric staining regions appear in eukaryotic metaphases. d. Pan-centromeric FISH in an extra-syncytial bell shaped metakaryotic nucleus of human fetal colonic epithelium, 12 weeks. Centromeric staining regions sum to about 23 per nucleus and appear to be paired (arrowed). e. Bell shaped metakaryotic nucleus in human colon adenocarcinoma presented in 3D. Note doublets of centromeres (green) and telomeres (red). f. Pan-telomeric FISH in an extra-syncytial bell shaped metakaryotic nucleus in human colonic epithelium, 12 weeks. Telomeric staining regions summed to about 23 in extra-syncytial nuclei and many appeared to be doublets (arrow). g. Pan-telomeric (red) and whole chromosome #18 (FITC, green) FISH in a syncytial bell shaped nucleus in human spinal cord ganglia, 9 weeks. Note two separate staining masses. Bar scale, 5 µm.