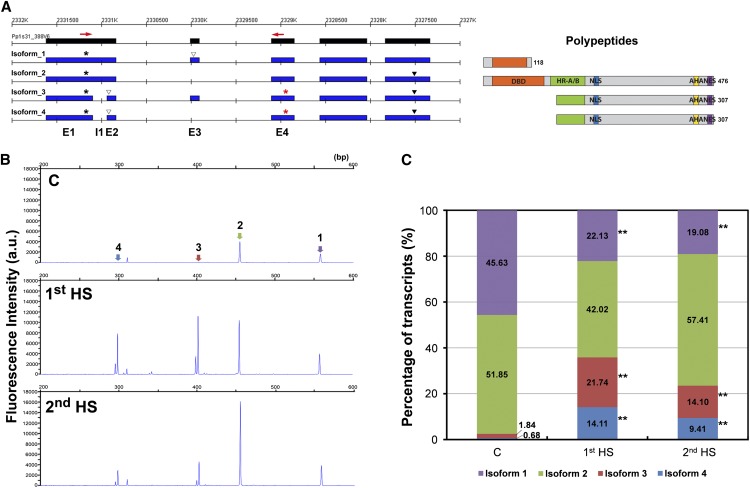
Figure 8.
AS events in the PpHSFA1-1 locus. A, Revised gene model and sequencing read mapping of the PpHSFA1-1 locus. Expressed exonic regions (black) and isoforms (blue) are shown. Asterisks in black over each isoform indicate the primary start codons; asterisks in red on isoforms 3 and 4 indicate potential downstream start codons. Solid and empty triangles represent stop codons and premature stop codons, respectively. Red arrows show the positions of the primer set for high-resolution RT-PCR. Polypeptides potentially encoded by the alternatively spliced isoforms are shown at right: orange, DBD; green, heptad repeat pattern of hydrophobic amino acid residues (HR-A/B); blue, nuclear localization signal (NLS); yellow, aromatic and large hydrophobic amino acid residues embedded in an acidic surround (AHA); and purple, nuclear export signal (NES). Sizes of the polypeptides are shown at the C-terminal end. B, Electrophoresis profiles of PCR products from the primer set indicated in A. The scale on the x axis represents the size (bp); the scale on the y axis indicates the relative fluorescence of the PCR products, reflecting transcript abundance. Peaks representing each isoform are labeled. a.u., Arbitrary unit; C, control. C, Relative expression levels of PpHSFA1-1 isoforms. Integrated peak areas of RT-PCR products from each isoform were used as the relative expression levels. The percentage of each isoform was calculated by dividing by the sum of all transcripts. Data from five biological replicates were used to determine statistical significance by doing arcsine transformation and Student’s t test. Significance is indicated by asterisks: **P < 0.01.